
Determination of the molar mass of acetic acid in benzene using freezing point depression is affected by:
A. complex formation
B. association
C. partial ionization
D. dissociation
Answer
560.1k+ views
Hint:The freezing point depression is a colligative property. The value of freezing point depression depends solely on the number of ions or components present on the system.
Complete step by step answer:
The given question is related to the colligative property of solutions. The freezing point depression is the lowering of freezing point of solvent due to addition of solute particles. The depression in freezing point ($\Delta {T_f}$) is expressed as
$\Delta {T_f} = i{K_f}m$
Where $i$ is the van’t Hoff factor, ${K_f}$ if the cryoscopic constant and $m$ is the molality.
The depression in freezing point depends on the factor $i$ which is the number of ions or components and the molality. The molality is the number of moles of acetic present per kg of the solvent. It is related to the molar mass of acetic acid.
The value of I depends on the fate of the solute added to the solvent system. The fate of solute decides whether the solute undergoes any dissociation or association with the solvent molecules. Due to such changes in solution the number of ions present in the solution changes and so the value of freezing point depression ($\Delta {T_f}$) changes.
The solvent given here is benzene which is a nonpolar solvent and the solute is acetic acid which is a polar molecule. These two components do not undergo any interaction like dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding with each other. But the acetic acid itself is able to undergo interaction with another acetic acid molecule.
This results in association of the acetic acid molecules due to hydrogen bonding interaction. Hence the actual number of acetic acid molecules decreases in the solution. The hydrogen bonding interaction is shown as:
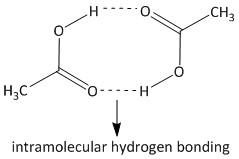
Due to the presence of such type of intramolecular interaction the actual number of molecules of acetic acid decreases to half. So the freezing point depression is erroneous. Hence the determination of molar mass of acetic acid is affected by association, i.e. option B is the correct answer.
Hence option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
The number of molecules should not be confused with the number of moles of solute. The freezing point depression does depend on the concentration of the solute and only on the total number of solute components in the mixture of solute and solvent. Unlike association, dissociation of a solute particle results in an increase of the number of molecules in the solution and as a result colligative property changes.
Complete step by step answer:
The given question is related to the colligative property of solutions. The freezing point depression is the lowering of freezing point of solvent due to addition of solute particles. The depression in freezing point ($\Delta {T_f}$) is expressed as
$\Delta {T_f} = i{K_f}m$
Where $i$ is the van’t Hoff factor, ${K_f}$ if the cryoscopic constant and $m$ is the molality.
The depression in freezing point depends on the factor $i$ which is the number of ions or components and the molality. The molality is the number of moles of acetic present per kg of the solvent. It is related to the molar mass of acetic acid.
The value of I depends on the fate of the solute added to the solvent system. The fate of solute decides whether the solute undergoes any dissociation or association with the solvent molecules. Due to such changes in solution the number of ions present in the solution changes and so the value of freezing point depression ($\Delta {T_f}$) changes.
The solvent given here is benzene which is a nonpolar solvent and the solute is acetic acid which is a polar molecule. These two components do not undergo any interaction like dipole-dipole or hydrogen bonding with each other. But the acetic acid itself is able to undergo interaction with another acetic acid molecule.
This results in association of the acetic acid molecules due to hydrogen bonding interaction. Hence the actual number of acetic acid molecules decreases in the solution. The hydrogen bonding interaction is shown as:

Due to the presence of such type of intramolecular interaction the actual number of molecules of acetic acid decreases to half. So the freezing point depression is erroneous. Hence the determination of molar mass of acetic acid is affected by association, i.e. option B is the correct answer.
Hence option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
The number of molecules should not be confused with the number of moles of solute. The freezing point depression does depend on the concentration of the solute and only on the total number of solute components in the mixture of solute and solvent. Unlike association, dissociation of a solute particle results in an increase of the number of molecules in the solution and as a result colligative property changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




