
Determine the number of optical isomers in the following compounds:
(A). $C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$
(B). $HOOC{(CHOH)_2}COOH$
(C). $HOOC{(CHOH)_3}COOH$
(D). ${H_3}C{(CHOH)_2}COOH$
(E). $C{H_3}CH(Br)CH(Br)COOH$
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: The different arrangement of the atoms of a molecule in space is termed as isomers. The term isomer is inspired from the Greek language in which it means as iso as same ane mers as parts. The credit for the discovery and the development of isomerism goes to J. Von Liebig of Germany in 1823.
Complete answer: Isomers are classified into structural isomers and stereoisomers.
Structural isomers are further classified into ionisation isomerism, solvent or hydrate isomerism, linkage isomerism, coordination isomerism, coordination position isomerism, and polymerisation isomerism.
Stereo isomers are further classified into geometrical isomers which are further classified into cis, trans, facial and meridonial isomers, and the optical isomers.
The optical isomers are of three types as (i) $[M\,{(AA)_3}\,]$ type with example as ${[Co{(en)_3}]^{3 + }}$ . (ii) $[M\,{(AA)_2}{B_2}\,]$ or $[M\,{(AA)_2}BC\,]$ type with example as $[CoC{l_2}{(en)_2}]$ . and (iii) $[M\,(AA){B_2}{C_2}\,]$ type with example as $[Co(en){(N{H_3})_2}C{l_2}]$ .
The most important criteria for a molecule to be optically active is the prosperity of the chirality. But chirality does not only mean different atoms attached to the central atom. For a molecule to be chiral, there should be absence of all the elements of symmetry.
If a molecule lacks elements of symmetry, the formula to calculate the optical isomer is ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ . $\forall \,n$ is the total number of chiral carbons.
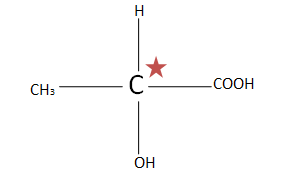
(A). $C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is one. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^1}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^0} \Rightarrow 1$. Thus only one optical isomer exists.
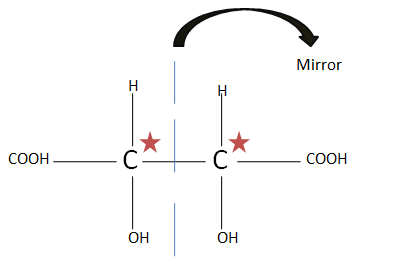
(B). $HOOC{(CHOH)_2}COOH$ as the plane of symmetry is present, there is no optical isomer present.
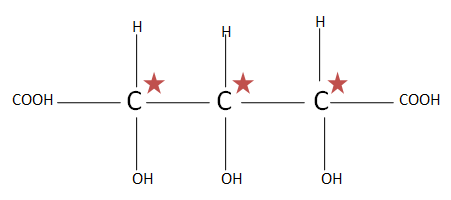
(C). $HOOC{(CHOH)_3}COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is three. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^3}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^2} \Rightarrow 4$
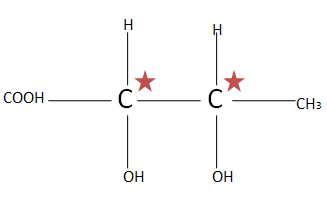
(D). ${H_3}C{(CHOH)_2}COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is two. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^2}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^1} \Rightarrow 2$
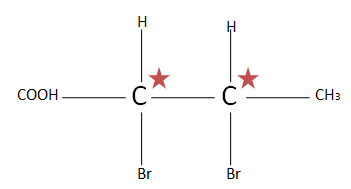
(E). $C{H_3}CH(Br)CH(Br)COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is two. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^2}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^1} \Rightarrow 2$
Note:
The elements of symmetry are (i) Axis of symmetry, (ii) Plane of symmetry, (iii) Improper axis of symmetry, (iv) Inversion. Iff any of the symmetric elements is present, then that molecule is considered to be achiral and does not possess optical activity.
Complete answer: Isomers are classified into structural isomers and stereoisomers.
Structural isomers are further classified into ionisation isomerism, solvent or hydrate isomerism, linkage isomerism, coordination isomerism, coordination position isomerism, and polymerisation isomerism.
Stereo isomers are further classified into geometrical isomers which are further classified into cis, trans, facial and meridonial isomers, and the optical isomers.
The optical isomers are of three types as (i) $[M\,{(AA)_3}\,]$ type with example as ${[Co{(en)_3}]^{3 + }}$ . (ii) $[M\,{(AA)_2}{B_2}\,]$ or $[M\,{(AA)_2}BC\,]$ type with example as $[CoC{l_2}{(en)_2}]$ . and (iii) $[M\,(AA){B_2}{C_2}\,]$ type with example as $[Co(en){(N{H_3})_2}C{l_2}]$ .
The most important criteria for a molecule to be optically active is the prosperity of the chirality. But chirality does not only mean different atoms attached to the central atom. For a molecule to be chiral, there should be absence of all the elements of symmetry.
If a molecule lacks elements of symmetry, the formula to calculate the optical isomer is ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ . $\forall \,n$ is the total number of chiral carbons.
(A). $C{H_3}CH(OH)COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is one. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^1}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^0} \Rightarrow 1$. Thus only one optical isomer exists.

(B). $HOOC{(CHOH)_2}COOH$ as the plane of symmetry is present, there is no optical isomer present.

(C). $HOOC{(CHOH)_3}COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is three. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^3}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^2} \Rightarrow 4$

(D). ${H_3}C{(CHOH)_2}COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is two. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^2}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^1} \Rightarrow 2$

(E). $C{H_3}CH(Br)CH(Br)COOH$ the total number of chiral carbons is two. So putting the numbers of chiral carbons present in formula ${2^n}^{ - 1}$ $ \Rightarrow {2^2}^{ - 1} \Rightarrow {2^1} \Rightarrow 2$

Note:
The elements of symmetry are (i) Axis of symmetry, (ii) Plane of symmetry, (iii) Improper axis of symmetry, (iv) Inversion. Iff any of the symmetric elements is present, then that molecule is considered to be achiral and does not possess optical activity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




