
What is the difference between a producer, secondary consumer, primary consumer and tertiary consumer?
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Producers and primary, secondary and tertiary consumers are the organisms that belong to the first, second, third and fourth trophic levels of the food chain respectively.
Each trophic level has a prey-predator relation with its preceding and succeeding level.
Complete answer:
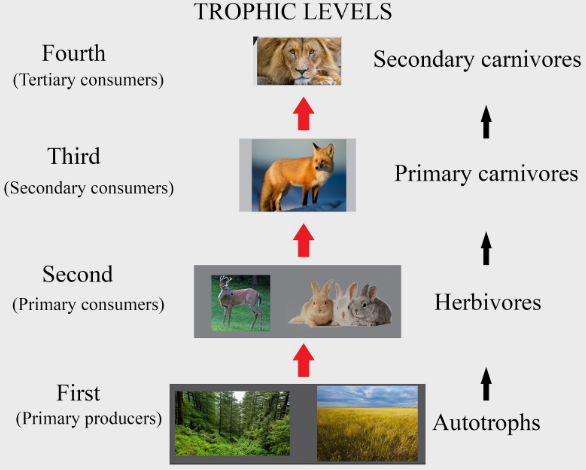
A food chain is a pictorial demonstration of the flow of energy and matter in the form of food. Each trophic level is categorised on the basis of the organism’s feeding habits and with transition from one level to another, a significant amount of energy is lost as heat. The levels start from the lowest-producers and move upwards to the tertiary consumers.
-Producers: This category of organisms include all autotrophic green plants that produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis, using the pigment chlorophyll. These organisms take energy from the sun to produce food which is stored as biomass. The first trophic level has the maximum stored biomass.
-Primary Consumers: The animals and plants that eat organisms belonging to the first trophic level are called primary consumers. They are also called herbivores as they feed on plants, for example: rabbits and cattle.
-Secondary Consumers: Animals that feed on herbivores belong to this group. They are also called primary carnivores, for example: snakes.
-Tertiary Consumers: These animals prey on primary carnivores and are thus also called secondary carnivores, for example: eagles, fox, etc.
Note:
Organisms do not belong to one single trophic level as their feeding habits differ. While one prey of a predator belongs to primary consumers, another prey of the same predator might belong to secondary consumers, altering the predator’s trophic level.
Each trophic level has a prey-predator relation with its preceding and succeeding level.
Complete answer:
A food chain is a pictorial demonstration of the flow of energy and matter in the form of food. Each trophic level is categorised on the basis of the organism’s feeding habits and with transition from one level to another, a significant amount of energy is lost as heat. The levels start from the lowest-producers and move upwards to the tertiary consumers.
-Producers: This category of organisms include all autotrophic green plants that produce their own food by the process of photosynthesis, using the pigment chlorophyll. These organisms take energy from the sun to produce food which is stored as biomass. The first trophic level has the maximum stored biomass.
-Primary Consumers: The animals and plants that eat organisms belonging to the first trophic level are called primary consumers. They are also called herbivores as they feed on plants, for example: rabbits and cattle.
-Secondary Consumers: Animals that feed on herbivores belong to this group. They are also called primary carnivores, for example: snakes.
-Tertiary Consumers: These animals prey on primary carnivores and are thus also called secondary carnivores, for example: eagles, fox, etc.
Note:
Organisms do not belong to one single trophic level as their feeding habits differ. While one prey of a predator belongs to primary consumers, another prey of the same predator might belong to secondary consumers, altering the predator’s trophic level.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




