
Difference between gametogenesis and embryogenesis.
Answer
524.8k+ views
Hint: Formation of gametes and embryo through different cell divisions resulting in either a haploid or diploid cells under a different process.
Complete answer:
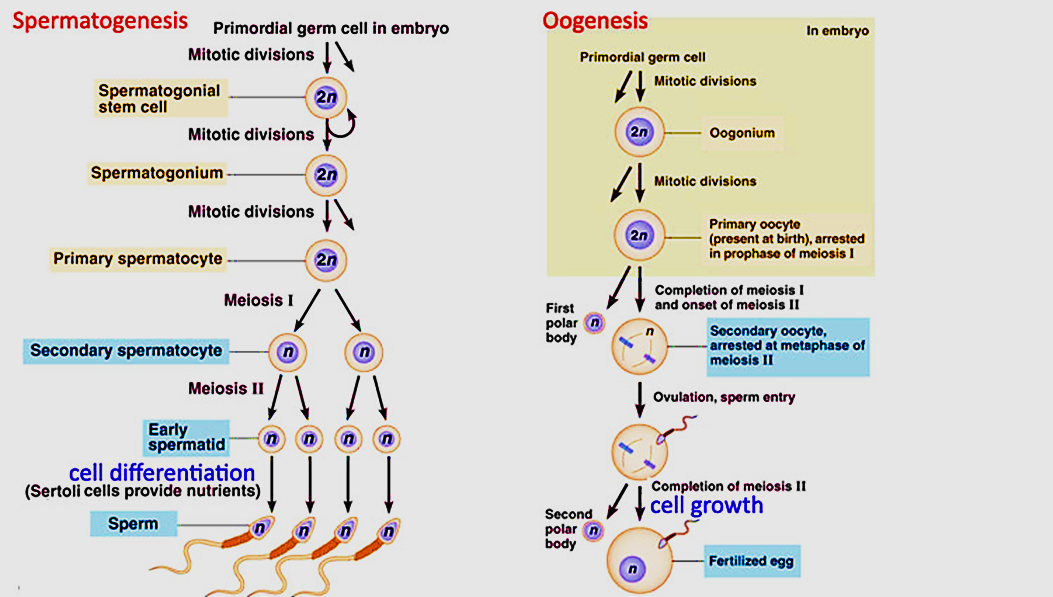
Gametogenesis is the formation of male or female gametes involving both mitosis and meiosis cell division in both Spermatogenesis (formation of male gamete: sperm) and Oogenesis (formation of female gamete: oocyte). Both result in the formation of Haploid cells known as gametes. It usually takes place during the pre-fertilization stage in testis (spermatogenesis) and ovaries (oogenesis) in animals and antheridia and archegonia in plants. Stages involved in gametogenesis include Gametocytogenesis, gametogenesis I, gametogenesis II and maturation. Gametogenesis involves two main phases: Cell division and maturation.
Figure 1: Gametogenesis
Embryogenesis on the other hand is the formation and development of embryos involving only mitosis cell division and the process is known as embryogenesis leading to organogenesis. It results in the formation of a diploid cell known as a zygote (unicellular) that develops into a multicellular embryo. It usually takes place post-fertilization (post fusion of gametes) in the female reproductive system in both animals and plants. Different stages of embryogenesis include Cleavage, gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Embryogenesis involves cell division to increase the number of cells, cell growth, and cell differentiation for the formation of different kinds of tissues.
Figure 2: Embryogenesis in Frog
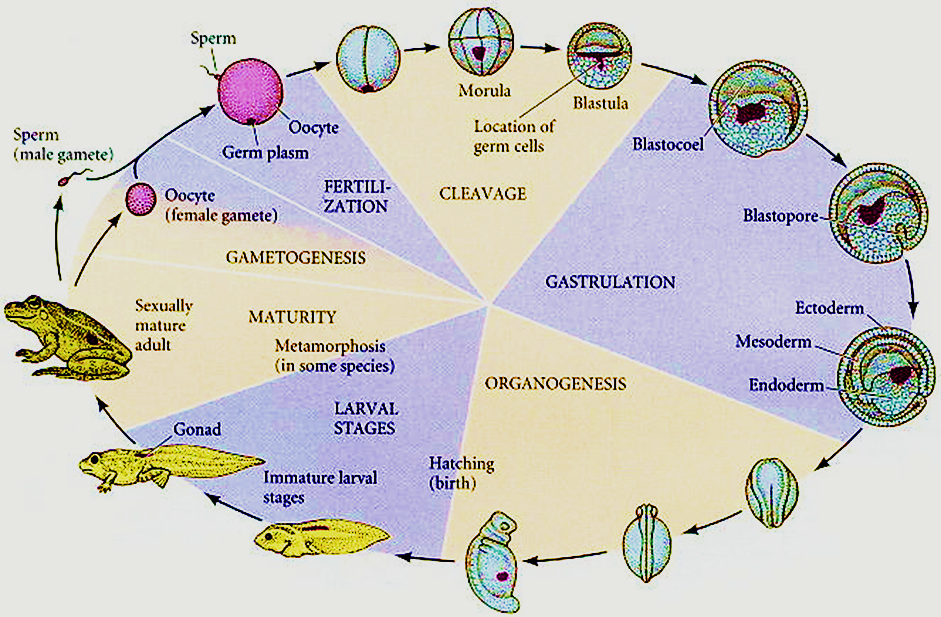
Table 1: Comparison between Gametogenesis and embryogenesis
Additional Information:
Gametogenesis involves four main steps:
1. Gametocytogenesis: diploid precursor cells of gametangium undergo cell division through mitosis.
2. Gametogenesis I: primary gametocytes undergo meiosis I
3. Gametogenesis II: secondary gametocytes undergo meiosis II
4. Maturation: secondary gametocytes undergo maturation to form either male or female gametes.
Embryogenesis also involves four main sequences of events:
1. Cleavage: involving cell division without any significant growth. Cells do not separate out and form a cell mass. Involves formation of morula and then blastula (a process known as blastulation)
2. Gastrulation: single-layer blastula develops into multilayer gastrula through cell differentiation (formation of ectoderm, endoderm, and mesodermal layer).
3. Neurulation: includes the transformation of neural plates (the basis of the neural system) into the neural tube.
4. Organogenesis: development of organs from germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) through cell differentiation and specialization.
Male gametes are known as spermatids that mature to form sperms. Oocytes are female mature gametes that are present as polar bodies and only one becomes a mature ovum every month.
Note: Both gametogenesis and embryogenesis are the sequential processes involved in sexual reproduction. Gametogenesis being pre-fertilization (before fusion of male and female gametes) event and embryogenesis is a post-fertilization event.
Complete answer:
Gametogenesis is the formation of male or female gametes involving both mitosis and meiosis cell division in both Spermatogenesis (formation of male gamete: sperm) and Oogenesis (formation of female gamete: oocyte). Both result in the formation of Haploid cells known as gametes. It usually takes place during the pre-fertilization stage in testis (spermatogenesis) and ovaries (oogenesis) in animals and antheridia and archegonia in plants. Stages involved in gametogenesis include Gametocytogenesis, gametogenesis I, gametogenesis II and maturation. Gametogenesis involves two main phases: Cell division and maturation.
Figure 1: Gametogenesis

Embryogenesis on the other hand is the formation and development of embryos involving only mitosis cell division and the process is known as embryogenesis leading to organogenesis. It results in the formation of a diploid cell known as a zygote (unicellular) that develops into a multicellular embryo. It usually takes place post-fertilization (post fusion of gametes) in the female reproductive system in both animals and plants. Different stages of embryogenesis include Cleavage, gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Embryogenesis involves cell division to increase the number of cells, cell growth, and cell differentiation for the formation of different kinds of tissues.
Figure 2: Embryogenesis in Frog

Table 1: Comparison between Gametogenesis and embryogenesis
| FEATURES | GAMETOGENESIS | EMBRYOGENESIS |
| Process for formation of | Male and female gametes | Embryo |
| Cell division includes | Mitosis and meiosis | Mitosis |
| Events include | Cell division and maturation | Cell division, cell growth, and Cell differentiation |
| End product | Haploid cell | Diploid cell |
| Event (timing) | Pre-fertilization event | Post fertilization event |
| Steps involved | Gametocytogenesis, gametogenesis I, gametogenesis II and maturation | Cleavage, gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis |
| Place of occurrence | Spermatogenesis (male reproductive organ)Oogenesis (in a female reproductive organ) | Female reproductive organ |
Additional Information:
Gametogenesis involves four main steps:
1. Gametocytogenesis: diploid precursor cells of gametangium undergo cell division through mitosis.
2. Gametogenesis I: primary gametocytes undergo meiosis I
3. Gametogenesis II: secondary gametocytes undergo meiosis II
4. Maturation: secondary gametocytes undergo maturation to form either male or female gametes.
Embryogenesis also involves four main sequences of events:
1. Cleavage: involving cell division without any significant growth. Cells do not separate out and form a cell mass. Involves formation of morula and then blastula (a process known as blastulation)
2. Gastrulation: single-layer blastula develops into multilayer gastrula through cell differentiation (formation of ectoderm, endoderm, and mesodermal layer).
3. Neurulation: includes the transformation of neural plates (the basis of the neural system) into the neural tube.
4. Organogenesis: development of organs from germ layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) through cell differentiation and specialization.
Male gametes are known as spermatids that mature to form sperms. Oocytes are female mature gametes that are present as polar bodies and only one becomes a mature ovum every month.
Note: Both gametogenesis and embryogenesis are the sequential processes involved in sexual reproduction. Gametogenesis being pre-fertilization (before fusion of male and female gametes) event and embryogenesis is a post-fertilization event.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




