
Differentiate between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: An exergonic reaction is a chemical reaction where their release of free energy and an endergonic reaction is a chemical reaction where energy is absorbed.
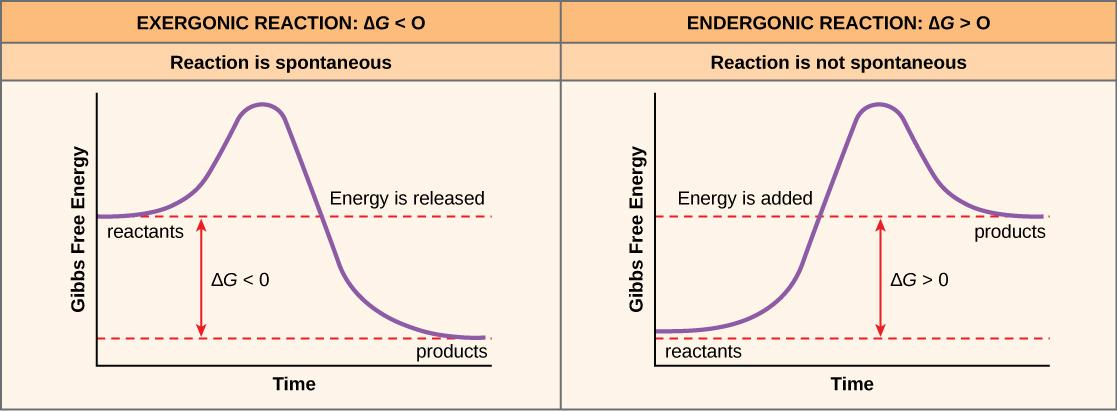
Complete answer: An exergonic reaction is a type of spontaneous reaction where there is ‘release ' of free, here free energy is negative (less than zero).
On the contrary, endergonic reactions are the reactions where energy enters the system, the free energy here is positive (greater than 0).
Free energy or Gibbs free energy (∆G) is nothing but the total available energy. If free energy is negative (-∆G), it means that energy is released and if it is positive, the energy is being absorbed/stored.
Note: Endergonic and exergonic reactions form the basis of the reactions happening in various organisms.
Catalysts may be required for some reactions to proceed at an observable speed.
Complete answer: An exergonic reaction is a type of spontaneous reaction where there is ‘release ' of free, here free energy is negative (less than zero).
On the contrary, endergonic reactions are the reactions where energy enters the system, the free energy here is positive (greater than 0).
Free energy or Gibbs free energy (∆G) is nothing but the total available energy. If free energy is negative (-∆G), it means that energy is released and if it is positive, the energy is being absorbed/stored.
| Exergonic reaction | Endergonic reaction |
| The exergonic reaction is a type of reaction in which free energy is released | Endergonic reactions are the type of reaction in which free energy is absorbed. |
| Here Gibbs free energy is negative | Here Gibbs free energy is positive |
| Exergonic reactions indicate that the energy is released in the system | Endergonic reactions indicate that the energy is absorbed by the system. |
| All the exothermic reactions are exergonic. | All endothermic reactions are endothermic. |
| Exergonic reactions do not require energy to begin | Endothermic reactions always require energy to begin. |
| It is a downhill reaction. | It is an uphill reaction |
| Fatty Acid Catabolism, Glycolysis, cellular respiration | DNA/RNA Synthesis, Protein synthesis, Fatty acid synthesis. |

Note: Endergonic and exergonic reactions form the basis of the reactions happening in various organisms.
Catalysts may be required for some reactions to proceed at an observable speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




