
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma based on their cell wall.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: These cells newly formed and become structurally and functionally specialized. They lose the ability to divide and are called permanent or mature cells, and the tissues formed from these cells are known as permanent tissues.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Classification of permanent tissues:
Permanent tissues are basically of two types, simple permanent and complex permanent.
Simple permanent tissues: It is made up of only one type of cell. Simple tissues found in plants are:
-Parenchyma
-Collenchyma
-Sclerenchyma
Note: Special type of parenchyma found in hydrophytes are called Aerenchyma i.e. plants living in water bodies.
Types of cells in sclerenchyma are: -
Sclerenchyma fibers: Highly elongated cells with pointed ends, these provide mechanical strength.
Sclereids: These are spherical, oval, or cylindrical cells. They occur in soft parts that are the pulp of fruits.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Classification of permanent tissues:
Permanent tissues are basically of two types, simple permanent and complex permanent.
Simple permanent tissues: It is made up of only one type of cell. Simple tissues found in plants are:
-Parenchyma
-Collenchyma
-Sclerenchyma

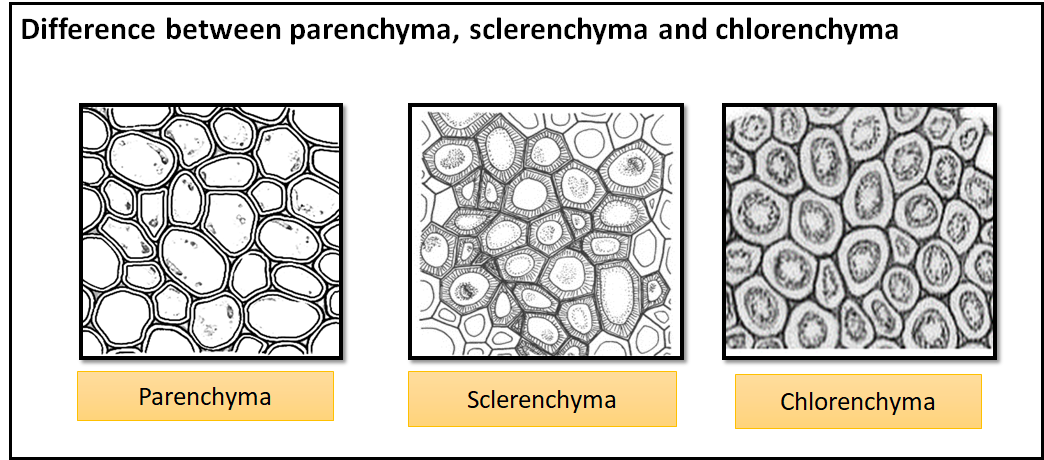
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Parenchymatous cells are the living cells and are generally isodiametric (nearly equal diameters). These cells may be spherical, oval, round, polygonal, or elongated in shape. | It is an elastic, living, mechanical tissue which may be oval, spherical, or polygonal in shape. | Sclerenchyma is a Greek word meaning hard tissue, they are usually dead without protoplast. Cells are elongated and narrow. |
| They are thinly walled. Their cell walls are made up of cellulose. These cells may either be closely packed with no or small intercellular space. | At the corner of the cells, thickening of the cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin develop due to which the cell wall becomes thick at the corners. These cells are closely packed with each other without intercellular spaces. | These have a highly thickened cell wall. Their wall consists of cellulose, hemicellulose, and specialized organic material lignin which provides mechanical strength to the plant and its parts. |
| Various functions are the storage of food, photosynthesis, and secretions of substances like renin, nectar, oil, etc. | The functions of collenchyma are to provide mechanical support to the growing parts of the plants such as young stems and take part in photosynthesis. | Functions are providing Mechanical strength. These are also present in fruit walls of nuts like walnut and almond, and seed coats of legumes. |
Note: Special type of parenchyma found in hydrophytes are called Aerenchyma i.e. plants living in water bodies.
Types of cells in sclerenchyma are: -
Sclerenchyma fibers: Highly elongated cells with pointed ends, these provide mechanical strength.
Sclereids: These are spherical, oval, or cylindrical cells. They occur in soft parts that are the pulp of fruits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




