
Differentiate between striated, un-striated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer
520.3k+ views
Hint: Our body is made up of different muscles or tissue that functions together and gives strength and structure to our body. The muscles are of different shape and size and found in different parts of the body. Some muscles can be controlled by us and some functions are automatic.
Complete answer:
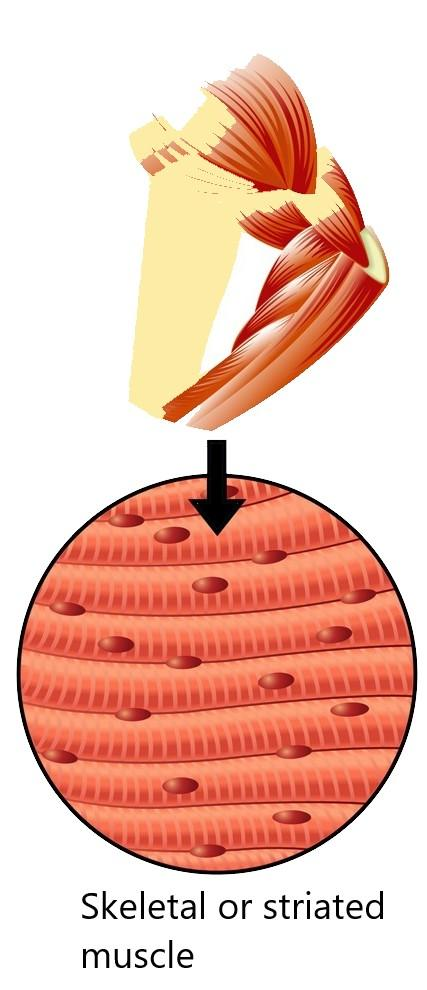
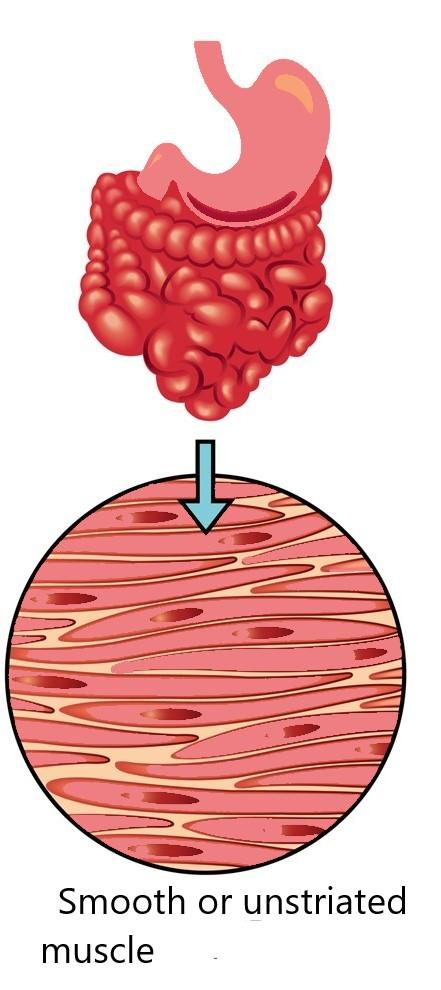
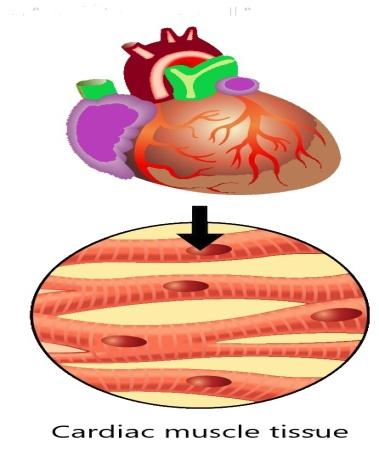
To answer this question, we have to first know about the muscles in the human body. There are approximately six hundred forty muscles inside a human body. Every muscle consists of one pair of identical bilateral muscles that present in both sides. The human body consists of three types of muscles; smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles. The smooth muscles form the wall of the intestine, blood vessels, uterus, and muscle of the inner eye. The cardiac muscles form the wall of the heart that controls the contraction of the heart, and the skeletal muscles attach the muscles to the bones.
Now, the difference between the striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles are:
Note:The cardiac and the smooth or unstriated muscles are involuntary as they cannot be controlled by us; they work automatically. For example the heart muscle, we cannot control the heart according to our need but we can control our skeletal muscle that is found in the hand and legs, therefore, striated muscles are called voluntary muscle.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we have to first know about the muscles in the human body. There are approximately six hundred forty muscles inside a human body. Every muscle consists of one pair of identical bilateral muscles that present in both sides. The human body consists of three types of muscles; smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles. The smooth muscles form the wall of the intestine, blood vessels, uterus, and muscle of the inner eye. The cardiac muscles form the wall of the heart that controls the contraction of the heart, and the skeletal muscles attach the muscles to the bones.
Now, the difference between the striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles are:
| Striated muscle | Unstriated muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| The shape of the striated muscles are cylindrical and multinucleated. | The shape of the unstriated muscles are spindle and uninucleated. | The shape of the cardiac muscles are cylindrical and uninucleated. |
| The striated muscles are found in the hand and legs part of the body. | The unstriated muscles are found in the mouth, stomach, intestine, iris, etc part of the body. | The cardiac muscles are found in the heart. |
| 
| 
|
Note:The cardiac and the smooth or unstriated muscles are involuntary as they cannot be controlled by us; they work automatically. For example the heart muscle, we cannot control the heart according to our need but we can control our skeletal muscle that is found in the hand and legs, therefore, striated muscles are called voluntary muscle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




