
Diols (I-IV) which react with \[Cr{{O}_{3}}\] in aqueous \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] and yield products that
readily undergo decarboxylation on heating, are:
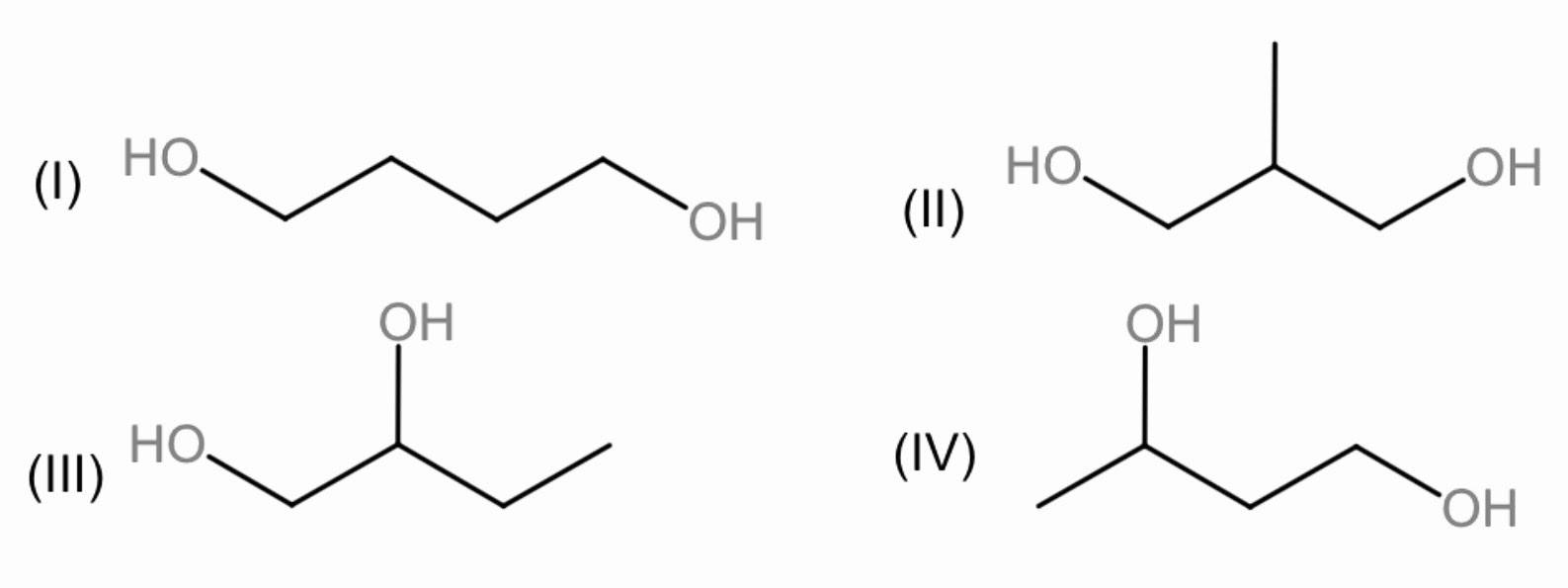
a.) I and II
b.) II and III
c.) II and IV
d.) I and IV

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: \[Cr{{O}_{3}}\] along with \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\] is used in the oxidation of primary alcohols to acid, secondary alcohols, that do not contain acid sensitive groups, to corresponding ketones and also the oxidation of primary allylic and benzylic alcohols gives aldehydes.
Complete step by step solution: Primary alcohols are those alcohols where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to only one single alkyl group, similarly secondary alcohol is a compound in which a hydroxyl group (OH), is attached to a carbon atom which has two other carbon atoms attached to it.
In the given diagram the primary alcohols are I and II whereas III and IV are having both primary and secondary alcohols.
Now the \[Cr{{O}_{3}}\] will oxidize the primary alcohols to acids and the secondary to ketones.
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide. Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. Decarboxylation occurs in the keto-acid groups.
Now, in figure I, the alcohols will be oxidized to carboxylic acids at primary positions, \[C{{O}_{2}}\] will be released and the decarboxylation can be done easily, but none of them are at beta-position. Therefore, decarboxylation will not take place.
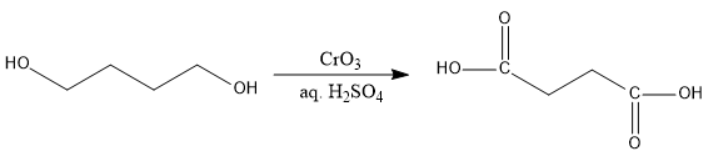
Similarly, in Figure II, alcohols will be oxidized into carboxylic acids, and both of them are present at beta-position to each other, thus, decarboxylation will take place.
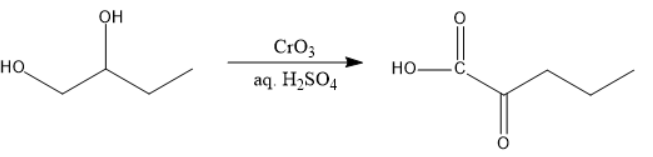
In Figure III, one alcohol will be oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other to ketone but they are present at alpha positions, thus, decarboxylation will not occur.
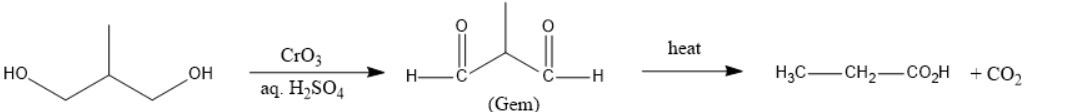
In figure IV, one alcohol will be oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other to ketone and both of them are present at Beta-positions, decarboxylation will take place.
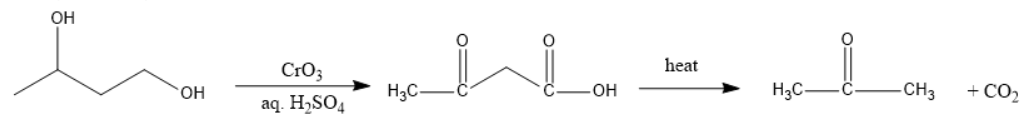
Therefore, from the above statements the correct answer is (c).
Note: beta-Keto acids are very unstable and readily undergo the elimination of carbon dioxide or simply decarboxylation under mild conditions. Ketones are obtained in these reactions.
Complete step by step solution: Primary alcohols are those alcohols where the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to only one single alkyl group, similarly secondary alcohol is a compound in which a hydroxyl group (OH), is attached to a carbon atom which has two other carbon atoms attached to it.
In the given diagram the primary alcohols are I and II whereas III and IV are having both primary and secondary alcohols.
Now the \[Cr{{O}_{3}}\] will oxidize the primary alcohols to acids and the secondary to ketones.
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide. Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. Decarboxylation occurs in the keto-acid groups.
Now, in figure I, the alcohols will be oxidized to carboxylic acids at primary positions, \[C{{O}_{2}}\] will be released and the decarboxylation can be done easily, but none of them are at beta-position. Therefore, decarboxylation will not take place.

Similarly, in Figure II, alcohols will be oxidized into carboxylic acids, and both of them are present at beta-position to each other, thus, decarboxylation will take place.

In Figure III, one alcohol will be oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other to ketone but they are present at alpha positions, thus, decarboxylation will not occur.

In figure IV, one alcohol will be oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other to ketone and both of them are present at Beta-positions, decarboxylation will take place.

Therefore, from the above statements the correct answer is (c).
Note: beta-Keto acids are very unstable and readily undergo the elimination of carbon dioxide or simply decarboxylation under mild conditions. Ketones are obtained in these reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




