
Discuss the generalised communication system with an appropriate block diagram.
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: Consider a telephone call, the person who speaks acts as the source of the message, his telephone transmits his voice through the telephone cables and is received by telephone of the listener who is the user of the information.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch the block diagram of a generalised communication system
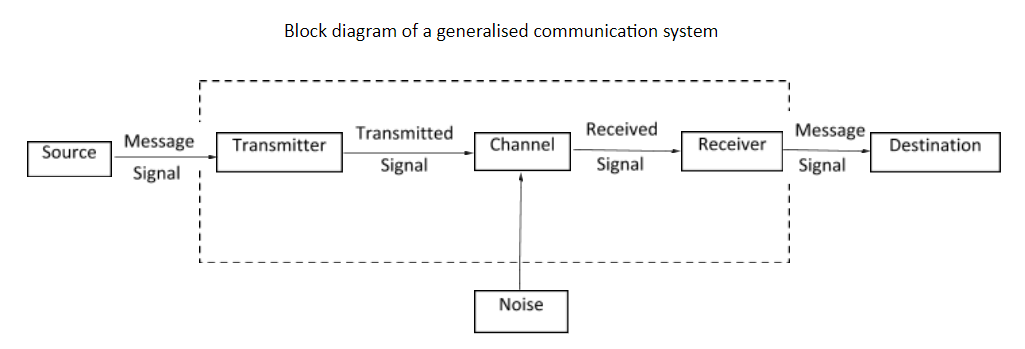
Step 2: Define communication
Communication refers to the act of sending and receiving information. Every communication system has 3 basic elements - transmitter, channel and receiver.
Step 3: Define each block in the diagram
The information converted in electrical form so that it is suitable for transmission is called a signal. Signals can be analog or digital. Signals which are continuous variations of voltage or current are called analog signals. Digital signals represent information as a sequence of discrete values.
Source produces the message signal that has to be transmitted.
Transmitter processes the incoming message signal so that it is suitable for transmission through a channel. The output of the transmitter is called transmitted signal.
Channel is a medium (can be wired or wireless medium) which accepts the transmitted signal from the transmitter as its input and produces a corrupted version of this input known as the received signal.
Noise refers to unwanted signals.
Receiver decodes the required message signal at the channel output.
Destination represents the user of the information. It accepts the reconstructed form of the original message.
Step 4: Explain the working of the communication system
The source produces a message signal which is fed to the transmitter. As the transmitted signal from the transmitter propagates through the channel, it gets corrupted with noise. Now, a corrupted version of the signal reaches the receiver. The receiver filters the transmitted signal from the noise to obtain the original message signal which is then sent to the user.
Additional Information:
There are two basic modes of communication: point-to-point and broadcast. In the former mode, communication occurs over a link between a transmitter and a receiver while in the latter, many receivers are present corresponding to a single transmitter. A telephone call is an example of point-to-point communication and radio is an example of broadcast mode.
Note: The arrow heads should point in the right direction in the block diagram. For a telephone call, the speaker and the listener interchange their role and therefore, the phone has a built-in transmitter and receiver. Also, the transmitted message should be an electrical signal and if it is not then, it must be converted to an electrical signal. A transducer fulfils this purpose, i.e., it converts one form of energy into another form of energy (here, electrical energy).
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch the block diagram of a generalised communication system

Step 2: Define communication
Communication refers to the act of sending and receiving information. Every communication system has 3 basic elements - transmitter, channel and receiver.
Step 3: Define each block in the diagram
The information converted in electrical form so that it is suitable for transmission is called a signal. Signals can be analog or digital. Signals which are continuous variations of voltage or current are called analog signals. Digital signals represent information as a sequence of discrete values.
Source produces the message signal that has to be transmitted.
Transmitter processes the incoming message signal so that it is suitable for transmission through a channel. The output of the transmitter is called transmitted signal.
Channel is a medium (can be wired or wireless medium) which accepts the transmitted signal from the transmitter as its input and produces a corrupted version of this input known as the received signal.
Noise refers to unwanted signals.
Receiver decodes the required message signal at the channel output.
Destination represents the user of the information. It accepts the reconstructed form of the original message.
Step 4: Explain the working of the communication system
The source produces a message signal which is fed to the transmitter. As the transmitted signal from the transmitter propagates through the channel, it gets corrupted with noise. Now, a corrupted version of the signal reaches the receiver. The receiver filters the transmitted signal from the noise to obtain the original message signal which is then sent to the user.
Additional Information:
There are two basic modes of communication: point-to-point and broadcast. In the former mode, communication occurs over a link between a transmitter and a receiver while in the latter, many receivers are present corresponding to a single transmitter. A telephone call is an example of point-to-point communication and radio is an example of broadcast mode.
Note: The arrow heads should point in the right direction in the block diagram. For a telephone call, the speaker and the listener interchange their role and therefore, the phone has a built-in transmitter and receiver. Also, the transmitted message should be an electrical signal and if it is not then, it must be converted to an electrical signal. A transducer fulfils this purpose, i.e., it converts one form of energy into another form of energy (here, electrical energy).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




