
Discuss the motion of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The motion of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field is based on the magnetic Lorentz force. Which states the important features of the magnetic force field and the expression can be written as $F=Bqv\sin \theta $.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Magnetic Lorentz force explains the force F experienced by the particle under the influence of the field. The special features of the force are:
i) The force F on the charge is zero if the charge is at rest. Which means only moving charges are affected by the field.
ii) The force is zero when the direction of motion of the charge is parallel or antiparallel to the field and the force is maximum when the charge is perpendicular to the field.
iii) The force is proportional to the magnitude of charge (q)
iv) It is proportional to the magnetic induction (B)
v) It is also proportional to the speed of charge (v)
vi) The direction of force is opposite for the charges of opposite sign
All these results are summed up as an expression and given as
$\vec { F } =q\left( \vec { v } \times \vec { B } \right)$
The magnitude can be written as $F=Bqv\sin \theta$
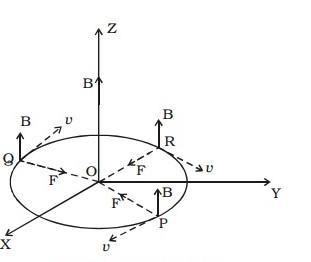
Let us now consider a uniform magnetic field B acting along the Z- axis. If a particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ moves in the XY plane. At a point, the velocity of a particle is v.
According to Lorentz force, $\vec { F } =q\left( \vec { v } \times \vec { B } \right)$. So, the force acts perpendicular to the plane consisting of $\vec { v }$ and $\vec { B }$. As the force is perpendicular to its velocity, it doesn't do any work. The magnitude of velocity is constant but direction changes. The force towards the center acts as the centripetal force and makes the particle move in a circular path.
As $\vec { v }$ and $\vec { B }$ are at right angles to each other,
$F=Bqv\sin {{90}^{\circ }}=Bqv$
The Lorentz force provides the centripetal force. Centripetal force is given as $\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
On equating both forces,
$Bqv=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
$r=\dfrac{mv}{Bq}$
From the equation, it is known that radius of the path is proportional to the mass and velocity of the particle.
Note: The equation also provides the angular frequency, $\omega =\dfrac{Bq}{m}$ from which the period of rotation can be calculated as $T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=\dfrac{2\pi m}{Bq}$. Both equations prove that angular frequency and period of rotation does not depend on the velocity or radius of the path.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Magnetic Lorentz force explains the force F experienced by the particle under the influence of the field. The special features of the force are:
i) The force F on the charge is zero if the charge is at rest. Which means only moving charges are affected by the field.
ii) The force is zero when the direction of motion of the charge is parallel or antiparallel to the field and the force is maximum when the charge is perpendicular to the field.
iii) The force is proportional to the magnitude of charge (q)
iv) It is proportional to the magnetic induction (B)
v) It is also proportional to the speed of charge (v)
vi) The direction of force is opposite for the charges of opposite sign
All these results are summed up as an expression and given as
$\vec { F } =q\left( \vec { v } \times \vec { B } \right)$
The magnitude can be written as $F=Bqv\sin \theta$

Let us now consider a uniform magnetic field B acting along the Z- axis. If a particle of charge ‘q’ and mass ‘m’ moves in the XY plane. At a point, the velocity of a particle is v.
According to Lorentz force, $\vec { F } =q\left( \vec { v } \times \vec { B } \right)$. So, the force acts perpendicular to the plane consisting of $\vec { v }$ and $\vec { B }$. As the force is perpendicular to its velocity, it doesn't do any work. The magnitude of velocity is constant but direction changes. The force towards the center acts as the centripetal force and makes the particle move in a circular path.
As $\vec { v }$ and $\vec { B }$ are at right angles to each other,
$F=Bqv\sin {{90}^{\circ }}=Bqv$
The Lorentz force provides the centripetal force. Centripetal force is given as $\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
On equating both forces,
$Bqv=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
$r=\dfrac{mv}{Bq}$
From the equation, it is known that radius of the path is proportional to the mass and velocity of the particle.
Note: The equation also provides the angular frequency, $\omega =\dfrac{Bq}{m}$ from which the period of rotation can be calculated as $T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=\dfrac{2\pi m}{Bq}$. Both equations prove that angular frequency and period of rotation does not depend on the velocity or radius of the path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




