
Distinguish between.
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) The upright and inverted pyramid
(d) Food chain and food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: A grazing food chain begins from plants. Plants produce biomass or organic matter while this organic matter is broken down by decomposers. The number or biomass in an ecological pyramid may increase or decrease while moving towards the apex. Matter and energy in an ecosystem can be transferred in a linear fashion or through an interconnection. The dead organic matter produced from plants and animals naturally first falls on the surface of the ground and later is taken by the soil for decomposition by detritivores. Biomass is produced by both producers and consumers.
Complete answer:
Before understanding what a grazing and detritus food chain is, let's first learn about the difference between a food chain and a food web.
Food chain and food web:
The order of transfer of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism in ecology is termed as ‘food chain.’ Examples of a food chain are the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain.
The natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of who eats whom in an ecological community is called a ‘food web.’
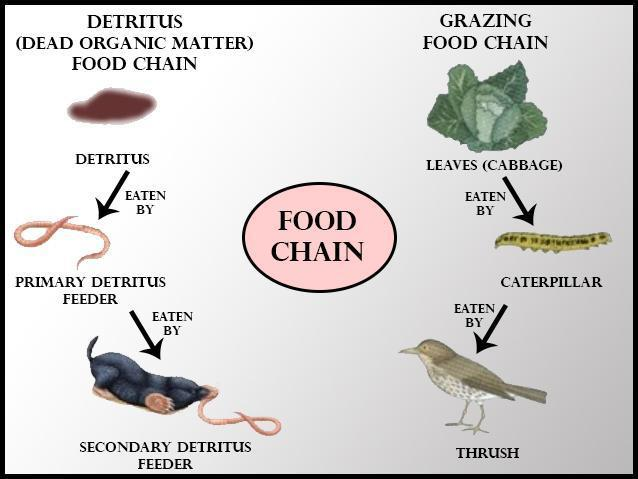
Grazing food chain and detritus food chain:
A simple ‘grazing food chain’ is the one which begins from producers like autotrophs, is followed by primary consumers-like herbivores and ends in secondary consumers like a human.
On the other hand, a detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter. It is formed by decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, primarily fungi, and bacteria.
Production and decomposition:
During photosynthesis, the total amount of biomass or organic matter generated per unit area over a period of time by plants is called ‘production.’
Microorganisms like decomposers break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients, this process is called ‘decomposition.’
Primary and secondary productivity:
The rate of production of biomass is called ‘productivity’. Hence, the productivity of autotrophs such as plants is called ‘primary productivity.’
The rate of generation of new organic matter by consumers is called ‘secondary productivity’.
Upright and inverted pyramid:
A graphical representation that illustrates the biomass or bio productivity at each trophic level in a given ecosystem is called an ecological pyramid. Relationships in a pyramid are expressed in terms of number, biomass, or energy. Usually, a pyramid is upright with a decrease in the number or biomass as we go up from the first trophic level to the apex. An example is a pyramid of biomass in a terrestrial ecosystem. However, sometimes the numbers may increase as we go to the next trophic levels leading to the formation of an inverted pyramid. An example of such a pyramid is the pyramid in an aquatic ecosystem.
Litter and detritus:
Dead organic material that has fallen on the surface of the soil such as fallen leaves, remains of animals and fecal matter is known as ‘litter’.
Dead organic matter such as flowers, leaves, bark, and dead remains of animals including fecal matter, which is found below the surface of the soil and eaten by detritivores or decomposers constitute ‘detritus.
Note:
- A food web is also called ‘consumer- resource system.’
- The decomposers in the detritus food chain meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also called ‘saprotrophs’.
- Detritus is the raw material for decomposition.
- Primary productivity depends on the species of plants inhabiting a particular area.
Complete answer:
Before understanding what a grazing and detritus food chain is, let's first learn about the difference between a food chain and a food web.
Food chain and food web:
The order of transfer of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism in ecology is termed as ‘food chain.’ Examples of a food chain are the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain.
The natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of who eats whom in an ecological community is called a ‘food web.’
Grazing food chain and detritus food chain:
A simple ‘grazing food chain’ is the one which begins from producers like autotrophs, is followed by primary consumers-like herbivores and ends in secondary consumers like a human.
On the other hand, a detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter. It is formed by decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, primarily fungi, and bacteria.
Production and decomposition:
During photosynthesis, the total amount of biomass or organic matter generated per unit area over a period of time by plants is called ‘production.’
Microorganisms like decomposers break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients, this process is called ‘decomposition.’
Primary and secondary productivity:
The rate of production of biomass is called ‘productivity’. Hence, the productivity of autotrophs such as plants is called ‘primary productivity.’
The rate of generation of new organic matter by consumers is called ‘secondary productivity’.
Upright and inverted pyramid:
A graphical representation that illustrates the biomass or bio productivity at each trophic level in a given ecosystem is called an ecological pyramid. Relationships in a pyramid are expressed in terms of number, biomass, or energy. Usually, a pyramid is upright with a decrease in the number or biomass as we go up from the first trophic level to the apex. An example is a pyramid of biomass in a terrestrial ecosystem. However, sometimes the numbers may increase as we go to the next trophic levels leading to the formation of an inverted pyramid. An example of such a pyramid is the pyramid in an aquatic ecosystem.
Litter and detritus:
Dead organic material that has fallen on the surface of the soil such as fallen leaves, remains of animals and fecal matter is known as ‘litter’.
Dead organic matter such as flowers, leaves, bark, and dead remains of animals including fecal matter, which is found below the surface of the soil and eaten by detritivores or decomposers constitute ‘detritus.

Note:
- A food web is also called ‘consumer- resource system.’
- The decomposers in the detritus food chain meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also called ‘saprotrophs’.
- Detritus is the raw material for decomposition.
- Primary productivity depends on the species of plants inhabiting a particular area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




