
Distinguish between conductor and semiconductor on the basis of band theory of solids.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Semiconductors are materials that have a very small forbidden energy gap that is the energy gap between the conduction and valence bands. By the increase in temperature, the electrons in the valence band acquire enough thermal energy and jump to the conduction band. Whereas in conductors these two overlap each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Semiconductors are solid substances that have conductivity between an insulator and of most metals. This change in conductivity is either due to the addition of an impurity or due to a change in temperature.
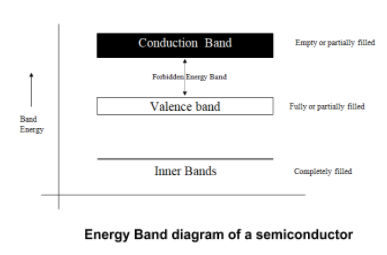
An enormously large number of energy levels closely spaced in a very small energy range constitutes an energy band. The highest energy band filled with valence electrons is called the valence band. The lowest unfilled allowed energy band next to the valence band is called the conduction band. The energy gap between valence and conduction band where no allowed energy levels for the electron exists is known as the forbidden energy gap. But the electrons can jump up or down from one energy level to another by gaining or losing energy, respectively.
At 0 K, the conduction band of the semiconductor is empty and the valence band is filled with electrons. So initially the material is an insulator at lower temperatures. However, the forbidden energy gap is very small. Thus, at room temperature, some valence electrons acquire enough energy and jump to the conduction band. [ by Boltzmann law, number of thermally excited electrons ]
Now in the conduction band, these electrons are free to conduct electricity, which thereby increases the conductivity and shifts the fermi level towards the conduction band.
A conductor on the other hand, has its last energy band occupied partially filled with electrons known as the conduction band. Now there can be a little gap between the completely filled valence band and the partially filled conduction band. Or like in most metals these two bands overlapping each other. Thus due to the presence of more than ample amounts of free electrons, conductors allow the flow of charge as well.
Therefore, semiconductors act as conductors when introduced to high temperature.
Note:
The things to be on the figure tips of students for further questions like this are:
- Energy Gap or Energy Band gap: An energy gap is an energy range in a material where no electron states exist. In other words, it is an energy range where the density of states vanishes.
- Understanding of the basic difference between metals, insulators, and semiconductors.
- Understanding of energy band diagrams.
Complete step by step answer:
Semiconductors are solid substances that have conductivity between an insulator and of most metals. This change in conductivity is either due to the addition of an impurity or due to a change in temperature.
An enormously large number of energy levels closely spaced in a very small energy range constitutes an energy band. The highest energy band filled with valence electrons is called the valence band. The lowest unfilled allowed energy band next to the valence band is called the conduction band. The energy gap between valence and conduction band where no allowed energy levels for the electron exists is known as the forbidden energy gap. But the electrons can jump up or down from one energy level to another by gaining or losing energy, respectively.
At 0 K, the conduction band of the semiconductor is empty and the valence band is filled with electrons. So initially the material is an insulator at lower temperatures. However, the forbidden energy gap is very small. Thus, at room temperature, some valence electrons acquire enough energy and jump to the conduction band. [ by Boltzmann law, number of thermally excited electrons ]
Now in the conduction band, these electrons are free to conduct electricity, which thereby increases the conductivity and shifts the fermi level towards the conduction band.

A conductor on the other hand, has its last energy band occupied partially filled with electrons known as the conduction band. Now there can be a little gap between the completely filled valence band and the partially filled conduction band. Or like in most metals these two bands overlapping each other. Thus due to the presence of more than ample amounts of free electrons, conductors allow the flow of charge as well.
Therefore, semiconductors act as conductors when introduced to high temperature.
Note:
The things to be on the figure tips of students for further questions like this are:
- Energy Gap or Energy Band gap: An energy gap is an energy range in a material where no electron states exist. In other words, it is an energy range where the density of states vanishes.
- Understanding of the basic difference between metals, insulators, and semiconductors.
- Understanding of energy band diagrams.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




