
Distinguish between X and Y chromosomes.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Humans usually have 23 pairs of chromosomes i.e. a total of 46 chromosomes. The autosomes (1-22 chromosome pairs) are the same in males and females. Females have two X chromosomes, whereas males have an X chromosome and a much smaller Y chromosome.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecule of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which contains a part or all of the genetic material of an organism is called Chromosome and pair 23 is dissimilar for males and females.
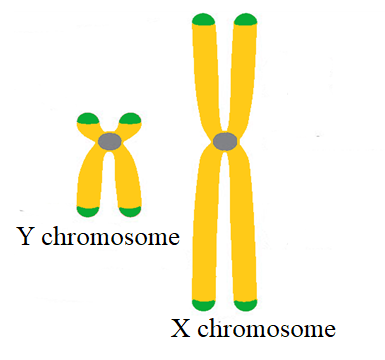
Difference between the X chromosome and Y chromosome:
Note: Multicellular organisms have special cells called gametes for reproduction which contain only half the number of chromosomes. So when gametes from two different parents combine during reproduction, it results in a new individual, which contains DNA (the genetic material passed from parents) and a re-established number of chromosomes. This process is done by many species to produce their offspring as it is the only means to ensure the continuity of a species.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecule of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) which contains a part or all of the genetic material of an organism is called Chromosome and pair 23 is dissimilar for males and females.
Difference between the X chromosome and Y chromosome:
| X chromosome | Y chromosome |
| Appear as X shape as they are metacentric and are longer compared to the Y chromosome. | Appear as Y shape as they are acrocentric and are shorter compared to the X chromosome. |
| It contains a large amount of euchromatin (a lightly packed form of chromatin). | It contains a small amount of euchromatin. |
| It contains a small amount of heterochromatin (condensed chromatin structure). | It contains a large amount of heterochromatin. |
| There is a large amount of DNA or active genes present in the X chromosome. | There is a small amount of DNA or active genes present in the Y chromosome. |
| The X chromosome contains over 1000 genes | The Y chromosome contains nearly 78 genes. |
| Genes present in the X chromosome shows criss cross inheritance. | Genes present in the Y chromosome shows linear inheritance. |
| X chromosomes are found in both genders. | Y chromosomes are found only in males. |

Note: Multicellular organisms have special cells called gametes for reproduction which contain only half the number of chromosomes. So when gametes from two different parents combine during reproduction, it results in a new individual, which contains DNA (the genetic material passed from parents) and a re-established number of chromosomes. This process is done by many species to produce their offspring as it is the only means to ensure the continuity of a species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




