
What is DNA? Describe the double helical structure of eukaryotic DNA.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: DNA is the basic component of the genetic material, because of which we inherit certain genes and characteristics of our ancestors. Eukaryotes are those organisms that have a well-defined nucleus.
Complete step by step answer:
DNA can be defined as “a group of molecules that is responsible for carrying and transmitting the hereditary materials or the genetic instructions from the parents to off-springs”.
Eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell.
The structure of DNA is given below –
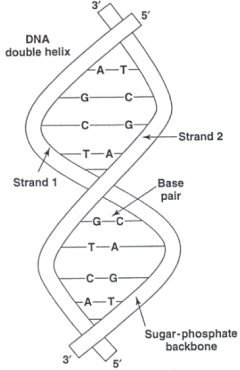
The term DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is a nucleic acid, which is composed of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a pentose (deoxyribose), a phosphate group and a nitrogen containing base (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine). The pentose sugar acts as a backbone. The nitrogenous base is responsible for the genetic code.
These nucleotides further connect together to make a single strand. Therefore, each strand has a backbone which is made up of alternating groups of sugar and phosphate groups. The bases link as pairs:
These base pairs link via hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases of the opposite strands wind around each other to form a twisted ladder-like structure. These two strands run in opposite directions. This structure is known as the double helical structure of eukaryotic DNA.
Additional Information: RNA is another type of nucleic acid. It stands for Ribonucleic acid.
Note: There are many differences between eukaryotic DNA and prokaryotic DNA, such as –
1. Prokaryotic DNA occurs as a covalently closed circular form of DNA. Whereas, eukaryotic DNA occurs as a linear form of DNA with two ends.
2. There is no formation of nucleosomes by prokaryotic DNA, whereas some nucleosomes are formed in eukaryotic DNA.
3. Prokaryotic DNA is found in the cytoplasm of the cell. Whereas, eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell.
Complete step by step answer:
DNA can be defined as “a group of molecules that is responsible for carrying and transmitting the hereditary materials or the genetic instructions from the parents to off-springs”.
Eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell.
The structure of DNA is given below –

The term DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is a nucleic acid, which is composed of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a pentose (deoxyribose), a phosphate group and a nitrogen containing base (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine). The pentose sugar acts as a backbone. The nitrogenous base is responsible for the genetic code.
These nucleotides further connect together to make a single strand. Therefore, each strand has a backbone which is made up of alternating groups of sugar and phosphate groups. The bases link as pairs:
Adenine – Thymine
Guanine - Cytosine
These base pairs link via hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases of the opposite strands wind around each other to form a twisted ladder-like structure. These two strands run in opposite directions. This structure is known as the double helical structure of eukaryotic DNA.
Additional Information: RNA is another type of nucleic acid. It stands for Ribonucleic acid.
Note: There are many differences between eukaryotic DNA and prokaryotic DNA, such as –
1. Prokaryotic DNA occurs as a covalently closed circular form of DNA. Whereas, eukaryotic DNA occurs as a linear form of DNA with two ends.
2. There is no formation of nucleosomes by prokaryotic DNA, whereas some nucleosomes are formed in eukaryotic DNA.
3. Prokaryotic DNA is found in the cytoplasm of the cell. Whereas, eukaryotic DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




