
What is DNA fingerprinting? Describe various steps involved in the same.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: On average, about 99.9 percent of the DNA between two humans is the same. It is due to the difference present in the 0.1 percent of the DNA that makes each individual unique.
Complete answer: DNA fingerprinting is a lab technique that is mainly used in order to find a connecting link of a suspect and their biological evidence.
1. A blood sample is collected after which DNA is extracted from the RBCs carefully.
2. With the help of various restriction enzymes (endonucleases and exonucleases), the DNA is processed and cut into fragments.
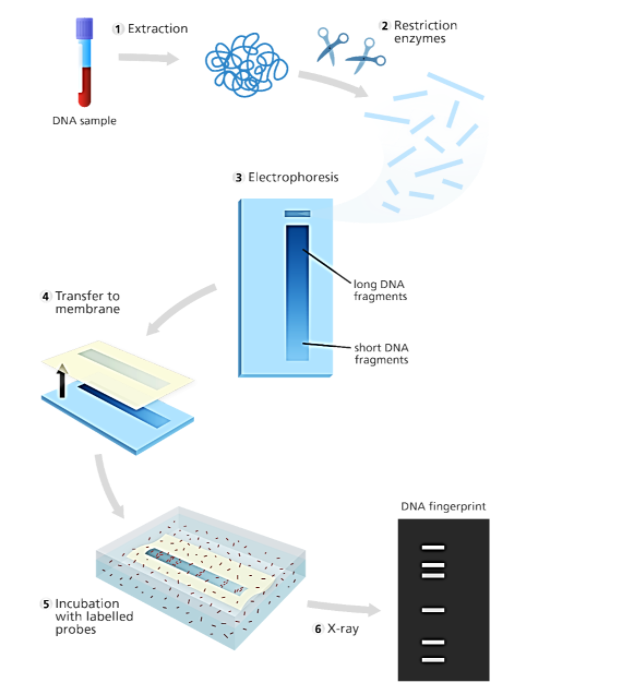
3. Next, these fragments are made to undergo agarose gel electrophoresis where they get according to their molecular weight separated into bands.
4. In the next step, using the southern blotting technique, the DNA bands are transferred into a thin nylon membrane after which the radioactive probe of DNA is prepared.
5. This DNA probe binds to specific DNA sequences onto the nylon membrane.
6. In order to detect the radioactive probes, X-ray film is introduced near the nylon membrane. In the last step, this X-ray film is developed and a sequence of bands can be seen which is essentially known as the fingerprint.
Note: A suspect generally leaves their biological evidence like fingerprints or footprints, and this sample is carefully collected and sent for analysis in labs.
If the two DNA profiles of the collected evidence and the person matches, then their crime can be proved and in case they don’t match then they can be proved innocent.
Another important application is to find out the paternal identity of a person.
Complete answer: DNA fingerprinting is a lab technique that is mainly used in order to find a connecting link of a suspect and their biological evidence.
1. A blood sample is collected after which DNA is extracted from the RBCs carefully.
2. With the help of various restriction enzymes (endonucleases and exonucleases), the DNA is processed and cut into fragments.

3. Next, these fragments are made to undergo agarose gel electrophoresis where they get according to their molecular weight separated into bands.
4. In the next step, using the southern blotting technique, the DNA bands are transferred into a thin nylon membrane after which the radioactive probe of DNA is prepared.
5. This DNA probe binds to specific DNA sequences onto the nylon membrane.
6. In order to detect the radioactive probes, X-ray film is introduced near the nylon membrane. In the last step, this X-ray film is developed and a sequence of bands can be seen which is essentially known as the fingerprint.
Note: A suspect generally leaves their biological evidence like fingerprints or footprints, and this sample is carefully collected and sent for analysis in labs.
If the two DNA profiles of the collected evidence and the person matches, then their crime can be proved and in case they don’t match then they can be proved innocent.
Another important application is to find out the paternal identity of a person.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




