
How does a lion's life depend on producers?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: A food chain is a network of links in a food web that starts with producers and ends with apex predators, detritivores, or decomposer animals. A food chain also demonstrates how species are connected by the food they consume. The food chain begins with producers followed by consumers and decomposers.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the food chain and its components.
i) Producers- Autotrophs, are organisms that produce their own food. They are the foundation of every food chain. It includes photosynthetic plants.
ii) Consumers- herbivores, carnivores and omnivores are species that consume both plants and animals. iii) Decomposers are creatures that get their energy from dead plants and animals.
The consumers include-
- The primary consumers(herbivores) are the animals that eat the producers. Example deer.
- The secondary consumers are meat-eating species (carnivores) that consume the primary consumers. Secondary users are typically larger and more numerous. Example tiger.
The food chain can be represented as:
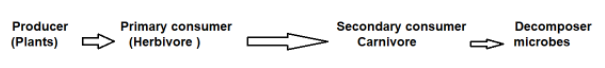
The lion which is a secondary consumer is indirectly dependent on the plants or the producers. They consume herbivores and omnivores like deer which feed on plants. So we can say that tigers indirectly receive energy from the plants or producers.
Note: When an organism is consumed, about half of the energy in food (possibly as much as 90%) is lost at each trophic stage, making being a higher order consumer less effective than being a primary consumer. As a result, energy flow from one trophic stage to the next, up the food chain, resembles a pyramid, with the base being broader and the top narrower.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the food chain and its components.
i) Producers- Autotrophs, are organisms that produce their own food. They are the foundation of every food chain. It includes photosynthetic plants.
ii) Consumers- herbivores, carnivores and omnivores are species that consume both plants and animals. iii) Decomposers are creatures that get their energy from dead plants and animals.
The consumers include-
- The primary consumers(herbivores) are the animals that eat the producers. Example deer.
- The secondary consumers are meat-eating species (carnivores) that consume the primary consumers. Secondary users are typically larger and more numerous. Example tiger.
The food chain can be represented as:

The lion which is a secondary consumer is indirectly dependent on the plants or the producers. They consume herbivores and omnivores like deer which feed on plants. So we can say that tigers indirectly receive energy from the plants or producers.
Note: When an organism is consumed, about half of the energy in food (possibly as much as 90%) is lost at each trophic stage, making being a higher order consumer less effective than being a primary consumer. As a result, energy flow from one trophic stage to the next, up the food chain, resembles a pyramid, with the base being broader and the top narrower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





