
How does a positive slope differ from a negative slope?
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: We first try to describe the relation between the slope of a curve and the characteristics of it being increasing, decreasing. We find the differentiation of the curve for $y=f\left( x \right)$. Depending on the value of slope we get the characteristics of the function.
Complete step by step answer:
We first try to find the general term of a function where $y=f\left( x \right)$. We express the terms as ${{t}_{n}}$, the ${{n}^{th}}$ term of the series.
We take differentiation of the function and find the slope of the function.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$ is the slope of the function.
Now, if the slope at any fixed point is negative which means $\dfrac{df}{dx}<0$ then the function is decreasing and if $\dfrac{df}{dx}>0$ then the function is increasing.
If the changes for the whole curve happens very rapidly then the function is not monotone.
Lets’ take as an example where $f\left( x \right)=2x$.
We find the slope of the function by taking $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2$ as \[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}\].
Now for any value of $x$, the value of $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2>0$.
The function is monotonically increasing the whole function.
If we change the function from $f\left( x \right)=2x$ to $f\left( x \right)=-2x$, the function becomes monotonically decreasing as $\dfrac{df}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -2x \right)=-2<0$ for any value of $x$.
We have an arbitrary curve Y= f(x). We took two points A and B.
The tangents at those points are valued positive and negative respectively.
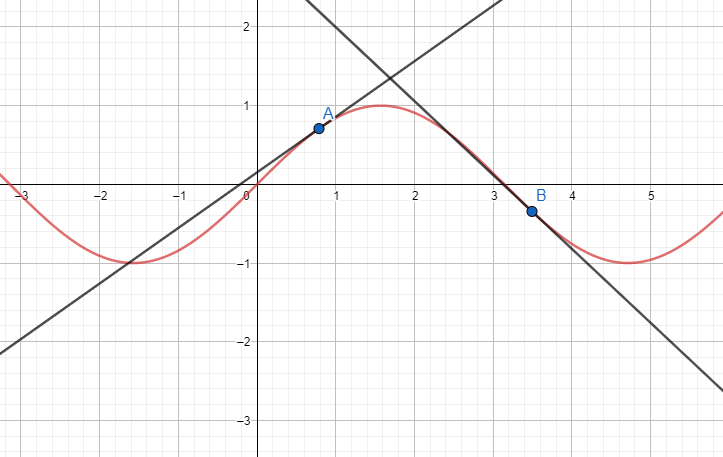
Note: We can also find the value of $x$ for which if we get ${{x}_{1}}>{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is increasing. If we find ${{x}_{1}}<{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is decreasing. The change of values is equal to the slope.
Complete step by step answer:
We first try to find the general term of a function where $y=f\left( x \right)$. We express the terms as ${{t}_{n}}$, the ${{n}^{th}}$ term of the series.
We take differentiation of the function and find the slope of the function.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$ is the slope of the function.
Now, if the slope at any fixed point is negative which means $\dfrac{df}{dx}<0$ then the function is decreasing and if $\dfrac{df}{dx}>0$ then the function is increasing.
If the changes for the whole curve happens very rapidly then the function is not monotone.
Lets’ take as an example where $f\left( x \right)=2x$.
We find the slope of the function by taking $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)$.
So, $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2$ as \[\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}\].
Now for any value of $x$, the value of $\dfrac{df}{dx}={{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=2>0$.
The function is monotonically increasing the whole function.
If we change the function from $f\left( x \right)=2x$ to $f\left( x \right)=-2x$, the function becomes monotonically decreasing as $\dfrac{df}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( -2x \right)=-2<0$ for any value of $x$.
We have an arbitrary curve Y= f(x). We took two points A and B.
The tangents at those points are valued positive and negative respectively.

Note: We can also find the value of $x$ for which if we get ${{x}_{1}}>{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is increasing. If we find ${{x}_{1}}<{{x}_{2}}$ and $f\left( {{x}_{1}} \right)>f\left( {{x}_{2}} \right)$, the curve is decreasing. The change of values is equal to the slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




