
How does an electric generator work?
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: An electric generator is an electronic device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, wind turbines, etc. When a closed coil of rectangular armature rotates in a uniform magnetic field of two strong poles then magnetic flux linked with coil changes continuously which in turns produces electric current.
Complete answer:
Electric generator is a device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy and it works on the principle of electromagnetic induction while the electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical work. The electric generator works in the reverse manner of an electric motor.
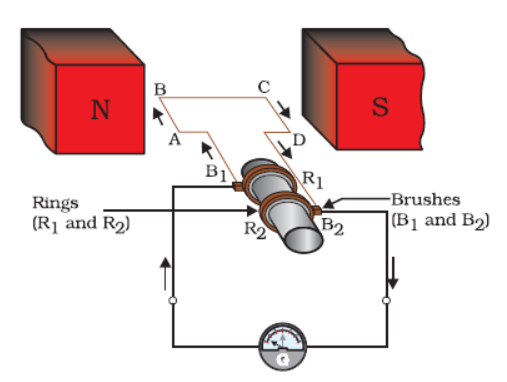
An electric generator consists of a closed rectangular coil ABCD placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet called North Pole and South Pole. The two ends of this closed coil are connected to the two slip rings named them as R1 and R2. These two conducting stationary brushes made up of carbon are named as B1 and B2 and are kept pressed on the rings R1 and R2, respectively. The axle will mechanically rotate from outside source to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field due to pole magnet. Two ends of the carbon brushes are connected to the galvanometer to show the flow of current in the given external circuit.
An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction phenomenon. According to this phenomenon, whenever a rectangular coil is rotated between the poles of a strong magnet, then the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes, due to this an induced current is set up in the coil, whose direction is given by Fleming’s right-hand rule and deflection in galvanometer justify the presence of current in the circuit.
After every half rotation of the rectangular coil the polarity of the current in the respective arms changes. Such a current, which direction changes continuously after regular intervals of time, is called an alternating current. So this device is called an AC generator.
To get a Direct current (DC, which does not change its direction with time), a split-ring type commentator must be used.
Note:
The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction and its magnitude remains constant with time, while the alternating current reverses its direction periodically and its magnitude also changes continuously. In India, the AC changes direction after every \[\dfrac{1}{100}\]second, so the frequency of AC is 50 Hz. An important advantage of AC over DC is that AC can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
Complete answer:
Electric generator is a device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy and it works on the principle of electromagnetic induction while the electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical work. The electric generator works in the reverse manner of an electric motor.

An electric generator consists of a closed rectangular coil ABCD placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet called North Pole and South Pole. The two ends of this closed coil are connected to the two slip rings named them as R1 and R2. These two conducting stationary brushes made up of carbon are named as B1 and B2 and are kept pressed on the rings R1 and R2, respectively. The axle will mechanically rotate from outside source to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field due to pole magnet. Two ends of the carbon brushes are connected to the galvanometer to show the flow of current in the given external circuit.
An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction phenomenon. According to this phenomenon, whenever a rectangular coil is rotated between the poles of a strong magnet, then the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes, due to this an induced current is set up in the coil, whose direction is given by Fleming’s right-hand rule and deflection in galvanometer justify the presence of current in the circuit.
After every half rotation of the rectangular coil the polarity of the current in the respective arms changes. Such a current, which direction changes continuously after regular intervals of time, is called an alternating current. So this device is called an AC generator.
To get a Direct current (DC, which does not change its direction with time), a split-ring type commentator must be used.
Note:
The difference between the direct and alternating currents is that the direct current always flows in one direction and its magnitude remains constant with time, while the alternating current reverses its direction periodically and its magnitude also changes continuously. In India, the AC changes direction after every \[\dfrac{1}{100}\]second, so the frequency of AC is 50 Hz. An important advantage of AC over DC is that AC can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




