
How does anisole react with bromine in ethanoic acid? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: You should know that; anisole is an electron withdrawing group. It undergoes electrophilic substitution. The halogenation will take place only at the ortho and para positions for anisole and the meta position is not included during this reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Anisole is an organic compound, which is also known by methoxybenzene. It has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}$.
The methoxy group present in anisole acts as an electron donating group and it will donate its electron density of the oxygen atom to the benzene ring and thus, the electron density on the benzene ring will increase. Further, this will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution, resulting in halogenation.
We should know that the methoxy group present in anisole is an ortho, para directing, thus it makes anisole ortho-para directing in nature. So, while reacting, the attacking group will attach to the ortho or para position with respect to the methoxy group in the ring.
Now, coming to ethanoic acid. As we know it is called acetic acid, which acts as a polar solvent for dissolving anisole.
So, we can write the chemical reaction of bromination of anisole as follows:
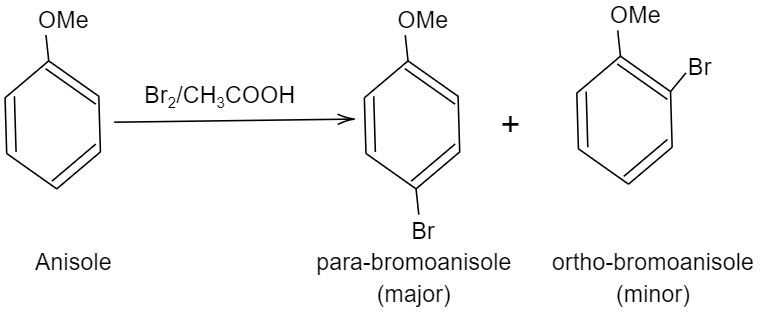
We can see, two products are formed i.e. para-bromoanisole (also written as $1-bromo-2-methoxybenzene$) and the other product is ortho-bromoanisole or $1-bromo-4-methoxybenzene$.
Note: Among these two products formed, para-bromoanisole is the major product and its yield will be around $90%$, ortho product formed is considered as the minor product due to the presence of steric hindrance in the ortho position (bulky methoxy group is present in the ortho group of the benzene ring).
Complete step by step solution:
Anisole is an organic compound, which is also known by methoxybenzene. It has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}$.
The methoxy group present in anisole acts as an electron donating group and it will donate its electron density of the oxygen atom to the benzene ring and thus, the electron density on the benzene ring will increase. Further, this will undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution, resulting in halogenation.
We should know that the methoxy group present in anisole is an ortho, para directing, thus it makes anisole ortho-para directing in nature. So, while reacting, the attacking group will attach to the ortho or para position with respect to the methoxy group in the ring.
Now, coming to ethanoic acid. As we know it is called acetic acid, which acts as a polar solvent for dissolving anisole.
So, we can write the chemical reaction of bromination of anisole as follows:

We can see, two products are formed i.e. para-bromoanisole (also written as $1-bromo-2-methoxybenzene$) and the other product is ortho-bromoanisole or $1-bromo-4-methoxybenzene$.
Note: Among these two products formed, para-bromoanisole is the major product and its yield will be around $90%$, ortho product formed is considered as the minor product due to the presence of steric hindrance in the ortho position (bulky methoxy group is present in the ortho group of the benzene ring).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




