
Why does carboxylic acid not give the reaction of the carbonyl group?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: You should think of the structures of carboxylic acid and carbonyl groups. There is a major role of resonance involved in the explanation of the answer to this question. Now try to answer this accordingly.
Complete step by step solution:
To answer this, firstly let’s see what a carbonyl group is. Compounds like aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl centres. It basically means that carbon will be double-bonded to an oxygen atom and the same carbon centre is attached to the alkyl group or other hydrogen atoms.
Aldehydes and ketones are examples of carbonyl groups. Carboxylic acids also contain carbonyl groups but do not show the reactions of carbonyl groups such as nucleophilic addition reactions like aldehydes and ketones. Let us discuss the reason behind it.
We know that carboxylic acids are RCOOH where R stands for an alkyl group. Examples of a carboxylic acid are acetic acid -$C{{H}_{3}}COOH$, propanoic acid - ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$ etc.
Due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH), the electrophilic character of carbonyl carbon is decreased due to the possibility of resonance, which in turns helps it gain extra stability.
Hence, the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is reduced. Therefore, we can say carboxylic acids do not give a characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group.
We can draw the resonance structure as-
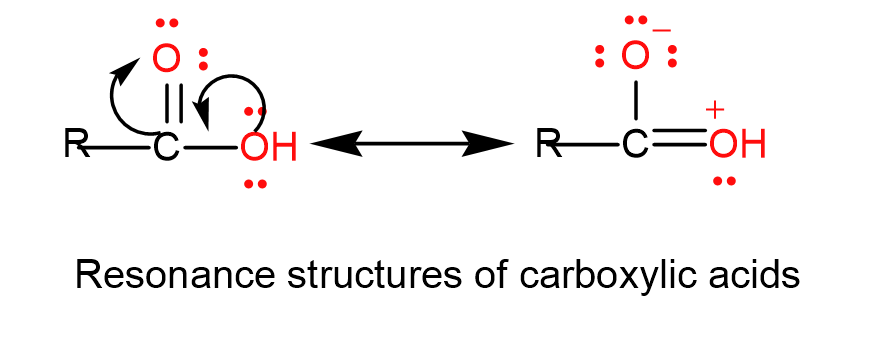
From the above discussion, we understand that the electrophilic character on the carbon atom decreases and it does not show characteristic reactions of carbonyls like nucleophilic addition reactions and this is the required answer.
Note: Carbonyls undergo nucleophilic addition whereas carboxylic acids undergo nucleophilic substitution. The nucleophile $O{{H}^{-}}$ is substituted by another nucleophile. The carbonyl group is polarised as oxygen is electronegative and pulls electron density towards itself. Here we can understand the basic difference between electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition. Electrophilic addition occurs where the group being added accepts an electron pair while nucleophilic addition occurs where the group being added donates an electron pair.
Complete step by step solution:
To answer this, firstly let’s see what a carbonyl group is. Compounds like aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl centres. It basically means that carbon will be double-bonded to an oxygen atom and the same carbon centre is attached to the alkyl group or other hydrogen atoms.
Aldehydes and ketones are examples of carbonyl groups. Carboxylic acids also contain carbonyl groups but do not show the reactions of carbonyl groups such as nucleophilic addition reactions like aldehydes and ketones. Let us discuss the reason behind it.
We know that carboxylic acids are RCOOH where R stands for an alkyl group. Examples of a carboxylic acid are acetic acid -$C{{H}_{3}}COOH$, propanoic acid - ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$ etc.
Due to the presence of the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH), the electrophilic character of carbonyl carbon is decreased due to the possibility of resonance, which in turns helps it gain extra stability.
Hence, the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is reduced. Therefore, we can say carboxylic acids do not give a characteristic reaction of the carbonyl group.
We can draw the resonance structure as-

From the above discussion, we understand that the electrophilic character on the carbon atom decreases and it does not show characteristic reactions of carbonyls like nucleophilic addition reactions and this is the required answer.
Note: Carbonyls undergo nucleophilic addition whereas carboxylic acids undergo nucleophilic substitution. The nucleophile $O{{H}^{-}}$ is substituted by another nucleophile. The carbonyl group is polarised as oxygen is electronegative and pulls electron density towards itself. Here we can understand the basic difference between electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition. Electrophilic addition occurs where the group being added accepts an electron pair while nucleophilic addition occurs where the group being added donates an electron pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




