
How does concave lens correct myopia?
A. increases the curvature of the eye lens.
B. Forms the image of the object at the retina.
C. Decreasing the elongation of the eyeball.
D. All of the above.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Myopia is nothing but nearsightedness. Nearsightedness itself gives idea about this disease. In this case, image of the object cant form at retina & forms in front of retina. To correct this we need diverging lens before light stick on eye lens. This artificial lens leads to form image at correct position.
Complete step by step answer:
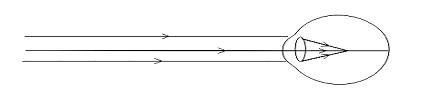
Nearby objects can be seen clearly.
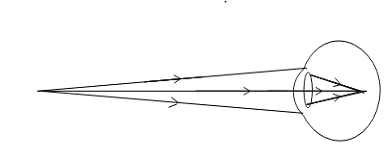
Myopic eye
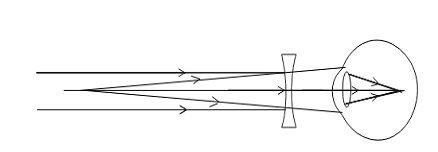
Correction of nearsightedness
As you know that, myopia is one type of eye disease. In this case, the eye can see nearby objects clearly but the distinct objects appear indistinct. This means that the eye shifts closer to the eye and the far point of the eye is not at infinity.
In nearsightedness, the image of the distant object forms in front of the retina as you can see in the above formula.
There are two reasons for this defect.
1) The curvature of the cornea and the eye lens increases. The muscles near the lens can not relax so that the converging power of the lens remains large.
2) The eyeball elongates to the distance between the lens and the retina increases.
This defect can be corrected by using spectacles with a concave lens of proper focal length. This lens diverges the incident rays and these diverged rays can be converged by the lens in the eye to form the image on the retina. The focal length of a concave lens is negative, so a lens with negative power is required for correcting nearsightedness. Depending on the magnitudes of their nearsightedness, the powers of the lens vary i.e. the power of a lens is different for different eyes.
Therefore option (B) is the correct answer i.e. image forms in front of the retina of the object in myopia.
Additional information:
The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object is at 25 cm. The position of the object at this distance is called the far point of eye. For a normal human eye, the far point is at infinity.
Note:
Other than nearsightedness, there is one more disease which is exactly opposite to it called farsightedness. Students may get confused between these two diseases. When a person will have both or suffer from both defects, in such case bifocal lenses are required to correct defects. The upper side of bifocal lenses corrects nearsightedness whereas the lower side of bifocal lenses corrects farsightedness.
Complete step by step answer:
Nearby objects can be seen clearly.

Myopic eye

Correction of nearsightedness

As you know that, myopia is one type of eye disease. In this case, the eye can see nearby objects clearly but the distinct objects appear indistinct. This means that the eye shifts closer to the eye and the far point of the eye is not at infinity.
In nearsightedness, the image of the distant object forms in front of the retina as you can see in the above formula.
There are two reasons for this defect.
1) The curvature of the cornea and the eye lens increases. The muscles near the lens can not relax so that the converging power of the lens remains large.
2) The eyeball elongates to the distance between the lens and the retina increases.
This defect can be corrected by using spectacles with a concave lens of proper focal length. This lens diverges the incident rays and these diverged rays can be converged by the lens in the eye to form the image on the retina. The focal length of a concave lens is negative, so a lens with negative power is required for correcting nearsightedness. Depending on the magnitudes of their nearsightedness, the powers of the lens vary i.e. the power of a lens is different for different eyes.
Therefore option (B) is the correct answer i.e. image forms in front of the retina of the object in myopia.
Additional information:
The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object is at 25 cm. The position of the object at this distance is called the far point of eye. For a normal human eye, the far point is at infinity.
Note:
Other than nearsightedness, there is one more disease which is exactly opposite to it called farsightedness. Students may get confused between these two diseases. When a person will have both or suffer from both defects, in such case bifocal lenses are required to correct defects. The upper side of bifocal lenses corrects nearsightedness whereas the lower side of bifocal lenses corrects farsightedness.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




