
How does electromagnetic induction work in a large audio speaker?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: Electromagnetic induction is the production of electric forces through a conductor under different type of magnetic fields and magnetic field keeps varying or magnetic field is stationary and a conductor is moving or we can say Electromagnetic Induction is a current produced because of voltage production (electromotive force EMF) due to a changing magnetic field.
Complete solution:
Permanent magnet and a light copper coil is used in audio speakers, coil is suspended in a gap between the both poles of a magnet and the coil moves back and forth due to induction which pushes the air and sound waves are produced. The moving coil loudspeaker is the most widely known and used form of loudspeaker and can be found in many recent devices.
In modern speaker electromagnet is used to convert electric signals of different strength into movement, by the magnet energy the copper coil moves and this work using induction.
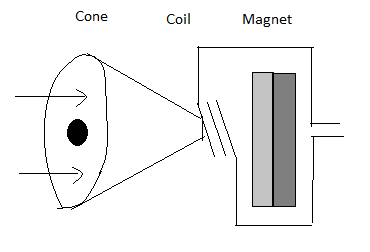
The following points are used to construct a loudspeaker:
1) Magnet-to provide fixed magnetic field against the field provided by the coil.
2) A circular frame which provides the basic structure.
3) Diaphragm (cone): it is used to transfer the vibrations of the moving coil to the air and present a large surface area.
4) Voice call, suspensions etc. to hold the voice coil in place, while allowing it to move freely in that area because the area is limited around the coil so to efficiently use the area so it can prevent touching the adjacent magnet.
Note:
The cone is a diaphragm that vibrates along with the coil in which sound is created and amplified by the diaphragm. To build a speaker there can be many variations of production according to the frequency range or for specific purposes that’s why by using different materials and designs we can retrieve different sounds.
Complete solution:
Permanent magnet and a light copper coil is used in audio speakers, coil is suspended in a gap between the both poles of a magnet and the coil moves back and forth due to induction which pushes the air and sound waves are produced. The moving coil loudspeaker is the most widely known and used form of loudspeaker and can be found in many recent devices.
In modern speaker electromagnet is used to convert electric signals of different strength into movement, by the magnet energy the copper coil moves and this work using induction.

The following points are used to construct a loudspeaker:
1) Magnet-to provide fixed magnetic field against the field provided by the coil.
2) A circular frame which provides the basic structure.
3) Diaphragm (cone): it is used to transfer the vibrations of the moving coil to the air and present a large surface area.
4) Voice call, suspensions etc. to hold the voice coil in place, while allowing it to move freely in that area because the area is limited around the coil so to efficiently use the area so it can prevent touching the adjacent magnet.
Note:
The cone is a diaphragm that vibrates along with the coil in which sound is created and amplified by the diaphragm. To build a speaker there can be many variations of production according to the frequency range or for specific purposes that’s why by using different materials and designs we can retrieve different sounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




