
Where does fertilization take place in human beings?
(a)Uterus
(b)Vagina
(c)Cervix
(d)Fallopian tube
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: In humans, fertilization takes place in the organ that is part of the female reproductive tract that receives the ovum, provides a suitable fertilizing environment, and transports it to the uterus. They are often referred to as salpinges.
Complete answer:
In humans, the steps of fertilization often require the joining of an egg and sperm. The male sperm fertilizes the female egg inside the body of the woman during natural conception. Just outside the ovary, fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube.
-The fertilized egg flows down the fallopian tube from there. An embryo will start to develop if it is inserted successfully in the uterus.
The Fallopian tubes are tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries and are part of the female reproductive system, also called uterine tubes or salpinges (singular salpinx).
In humans, fertilization occurs in the Fallopian tube. The sperm can swim and come into contact with the zona pellucida. It releases hormones/secretions that cause membrane changes and hydrolyzes the membrane of the ovum.
One sperm enters and prevents the entrance of other sperm, ensuring that the ovum is fertilized by only one sperm and avoiding polyspermy. Sperm entry causes the completion of the second ovum forming meiotic division and the second polar body. The haploid nucleus of sperm fuses with that of the ovum. Diploid zygote formation occurs, thereby completing the fertilization process.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Fallopian tube’.
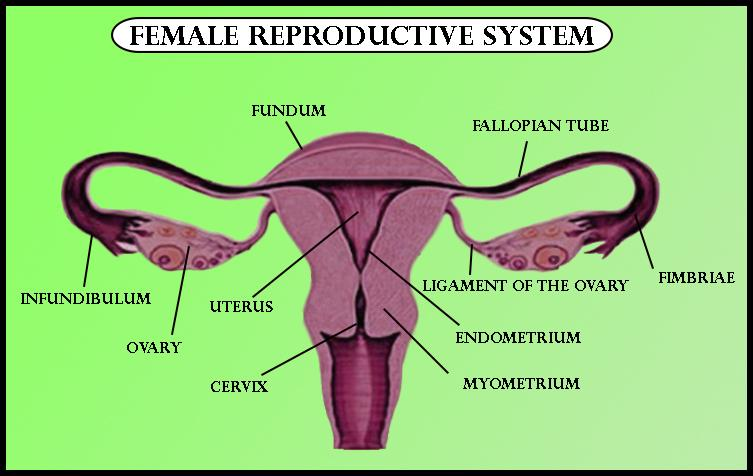
Note: A simple columnar epithelium with hair-like extensions called cilia that hold the fertilized egg is the fallopian tube. In other species, an oviduct is the equivalent of a fallopian tube. Four sections are made of the Fallopian tube. These are the infundibulum near the ovary with its corresponding fimbriae, the ampulla representing the important portion of the lateral tube, the isthmus, the narrower part of the tube that connects to the uterus, and the interstitial (or intramural) part, the narrowest part of the uterine tube that crosses the muscles of the uterus, defined from near the ovaries to inwards near the uterus. A fallopian tube has an average length of 11 to 12 cm.
Complete answer:
In humans, the steps of fertilization often require the joining of an egg and sperm. The male sperm fertilizes the female egg inside the body of the woman during natural conception. Just outside the ovary, fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube.
-The fertilized egg flows down the fallopian tube from there. An embryo will start to develop if it is inserted successfully in the uterus.
The Fallopian tubes are tubes that extend from the uterus to the ovaries and are part of the female reproductive system, also called uterine tubes or salpinges (singular salpinx).
In humans, fertilization occurs in the Fallopian tube. The sperm can swim and come into contact with the zona pellucida. It releases hormones/secretions that cause membrane changes and hydrolyzes the membrane of the ovum.
One sperm enters and prevents the entrance of other sperm, ensuring that the ovum is fertilized by only one sperm and avoiding polyspermy. Sperm entry causes the completion of the second ovum forming meiotic division and the second polar body. The haploid nucleus of sperm fuses with that of the ovum. Diploid zygote formation occurs, thereby completing the fertilization process.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Fallopian tube’.
Note: A simple columnar epithelium with hair-like extensions called cilia that hold the fertilized egg is the fallopian tube. In other species, an oviduct is the equivalent of a fallopian tube. Four sections are made of the Fallopian tube. These are the infundibulum near the ovary with its corresponding fimbriae, the ampulla representing the important portion of the lateral tube, the isthmus, the narrower part of the tube that connects to the uterus, and the interstitial (or intramural) part, the narrowest part of the uterine tube that crosses the muscles of the uterus, defined from near the ovaries to inwards near the uterus. A fallopian tube has an average length of 11 to 12 cm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




