
How does Gauss law work inside a conducting sphere?
Answer
557.4k+ views
Hint: An electric conductor has a very large number of charges that moves freely inside the sphere. In the conducting sphere, at all the points inside the sphere, the electric field is zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a uniformly charged sphere. The uniformly charged sphere has a radius of $R$. It has a total charge $Q$. The electric field inside the sphere can be found using the Gauss law.
Have the diagram for reference. Consider the point $P$ that is inside the shell that is placed at the distance $r$ from the center.
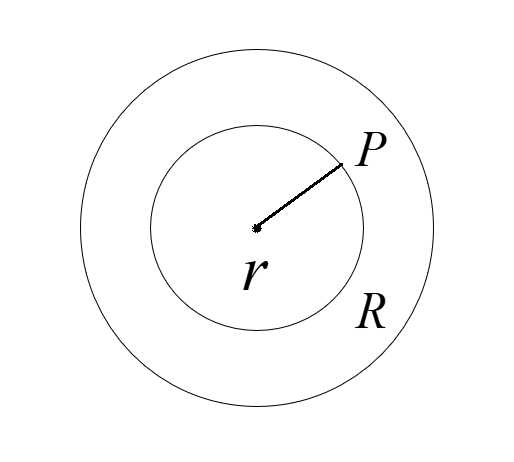
In the diagram, for the points inside the spherical sphere, a spherical gaussian surface is drawn smaller than the spherical sphere
The gaussian surface is drawn around the sphere with the radius. Now let us apply the gauss law. If a charge $Q$ is enclosed an arbitrary closed surface, then the total electric flux through the closed surface is,
$ \Rightarrow {\phi _E} = \oint {\overrightarrow E .d\overrightarrow A } $
Applying the gauss law,
$ \Rightarrow \oint {\overrightarrow E .d\overrightarrow A = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}} $
Substitute the value of the area in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Gaussian surface encloses no charge, that is $Q = 0$ . Substitute the charge value in the equation,
$ \Rightarrow E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{0}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Zero divided by any number is zero. The value of the electric field will become zero. That is,
$ \Rightarrow E = 0$
From this, we are able to understand that the electric field due to the uniformly charged sphere is zero at all the points inside the shell.
Note:
Suppose if the electric field inside the sphere is not zero then there will be a force acting on the mobile carriers due to the electric field. Due to this, there will be a net motion of the mobile charge carriers that contradicts the conductor being in the electrostatic equilibrium.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a uniformly charged sphere. The uniformly charged sphere has a radius of $R$. It has a total charge $Q$. The electric field inside the sphere can be found using the Gauss law.
Have the diagram for reference. Consider the point $P$ that is inside the shell that is placed at the distance $r$ from the center.

In the diagram, for the points inside the spherical sphere, a spherical gaussian surface is drawn smaller than the spherical sphere
The gaussian surface is drawn around the sphere with the radius. Now let us apply the gauss law. If a charge $Q$ is enclosed an arbitrary closed surface, then the total electric flux through the closed surface is,
$ \Rightarrow {\phi _E} = \oint {\overrightarrow E .d\overrightarrow A } $
Applying the gauss law,
$ \Rightarrow \oint {\overrightarrow E .d\overrightarrow A = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}} $
Substitute the value of the area in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Gaussian surface encloses no charge, that is $Q = 0$ . Substitute the charge value in the equation,
$ \Rightarrow E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{0}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Zero divided by any number is zero. The value of the electric field will become zero. That is,
$ \Rightarrow E = 0$
From this, we are able to understand that the electric field due to the uniformly charged sphere is zero at all the points inside the shell.
Note:
Suppose if the electric field inside the sphere is not zero then there will be a force acting on the mobile carriers due to the electric field. Due to this, there will be a net motion of the mobile charge carriers that contradicts the conductor being in the electrostatic equilibrium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




