
Does light travel in a straight line?
Answer
476.7k+ views
Hint: Light waves keep traveling in a straight line just like any other wave, this is the reason why we call it light ray since ray is a mathematical term used for a straight line. Light may deviate from its original path because of diffraction, although the diffraction is minimum because of a smaller wavelength.Hence deviation from its original path due to diffraction is also not that big because of this we can assume that light travels in a straight line.
Complete answer:
Diffraction of light: It is the phenomenon of light that is used to explain its bending around a sharp corner or aperture of size comparable to the wavelength of the light wave.As explained above one of the fundamental properties of the light wave is that it travels in a straight line but if the light wave is incident on an object, it will change its path slightly because of diffraction.
Although the deviation from its original path will be very small since the wavelength of the light ray is very small (Wavelength of visible light is in order of \[{10^{ - 6}}m\] or \[\mu m\] whereas the normal size is measured either in meter or cm).This is the reason why we assume that light always travels in straight light.
Additional information: These are some of the significant properties of light:
-Light-ray travels in a straight line.
-In a vacuum speed of light is \[3 \times {\text{ }}{10^8}m/s.\]
-Speed of light is greater than the speed of sound,
-Light is an electromagnetic wave and has both particles as well as wave nature.
-When light is reflected from a surface the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
-Light-ray shows properties like reflection, refraction (Snell’s law), Total internal reflection, interference, diffraction, dispersion, scattering & polarization.
Note:We know that the audible range of frequencies for a sound wave is between \[20{\text{ }}Hz{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}20,000{\text{ }}Hz\], which means the wavelength of the audible wave is between \[15{\text{ }}m{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}15{\text{ }}mm\] respectively. This is a reason why we observe the observer phenomena of diffraction for sound waves more often compared to light waves. Either for sound waves, the deviation due to any obstacle is very large compared to light rays.Also light may deviate from its original path because of refraction, reflection, or scattering. But during these process as well light always travel along a straight line as shown in the figure below:
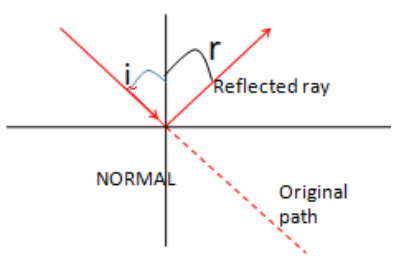
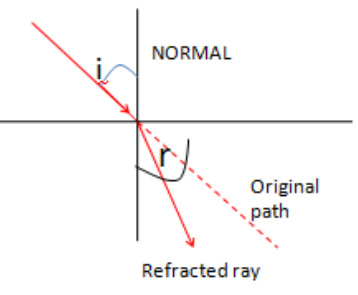
Here fig A represents a reflected ray in which \[i\] is the angle of reflection and \[r\] is the angle of reflection. Similarly, fig B represents refracted ray, in which \[i\] is the angle of incidence and \[r\] is the angle of refraction.
Complete answer:
Diffraction of light: It is the phenomenon of light that is used to explain its bending around a sharp corner or aperture of size comparable to the wavelength of the light wave.As explained above one of the fundamental properties of the light wave is that it travels in a straight line but if the light wave is incident on an object, it will change its path slightly because of diffraction.
Although the deviation from its original path will be very small since the wavelength of the light ray is very small (Wavelength of visible light is in order of \[{10^{ - 6}}m\] or \[\mu m\] whereas the normal size is measured either in meter or cm).This is the reason why we assume that light always travels in straight light.
Additional information: These are some of the significant properties of light:
-Light-ray travels in a straight line.
-In a vacuum speed of light is \[3 \times {\text{ }}{10^8}m/s.\]
-Speed of light is greater than the speed of sound,
-Light is an electromagnetic wave and has both particles as well as wave nature.
-When light is reflected from a surface the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
-Light-ray shows properties like reflection, refraction (Snell’s law), Total internal reflection, interference, diffraction, dispersion, scattering & polarization.
Note:We know that the audible range of frequencies for a sound wave is between \[20{\text{ }}Hz{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}20,000{\text{ }}Hz\], which means the wavelength of the audible wave is between \[15{\text{ }}m{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}15{\text{ }}mm\] respectively. This is a reason why we observe the observer phenomena of diffraction for sound waves more often compared to light waves. Either for sound waves, the deviation due to any obstacle is very large compared to light rays.Also light may deviate from its original path because of refraction, reflection, or scattering. But during these process as well light always travel along a straight line as shown in the figure below:


Here fig A represents a reflected ray in which \[i\] is the angle of reflection and \[r\] is the angle of reflection. Similarly, fig B represents refracted ray, in which \[i\] is the angle of incidence and \[r\] is the angle of refraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




