
What does meso mean in organic chemistry?
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: Let us first get some ideas about organic chemistry. Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds with covalent bonds between carbon atoms. The chemical composition and formula of a substance are determined by studying its structure.
Complete answer:
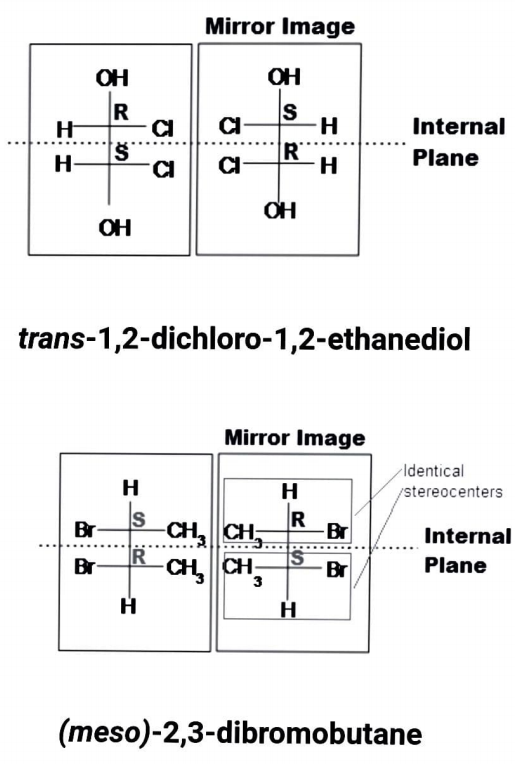
Meso compounds have several chiral centres and are achiral compounds. Despite its stereocenters, it is optically inactive since it is superimposed on its mirror image.A meso compound should have two or more equivalent substituted stereocenters in general. In addition, the compound is divided in half by an internal symmetry plane. The internal mirror reflects the two halves back at each other. Stereocenters' stereochemistry can "cancel out." What this implies is that when a compound is divided into two symmetrical sides by an internal plane, the stereochemistry of the left and right sides should be opposite, resulting in optically inactive results. It's possible that cyclic compounds are also meso.
Let’s see how we can identify meso.
If A is a meso compound, it must have at least two stereocenters, an internal plane, and R and S stereochemistry.
Look for an internal plane, also known as an internal mirror, that runs through the compound.
The stereochemistry (e.g., R or S) is extremely important in deciding whether or not a compound is a meso compound. Since a meso compound is optically inactive, the stereochemistry of the two can balance out. In a meso compound with two stereocenters, for example, R cancels out S.
Note:
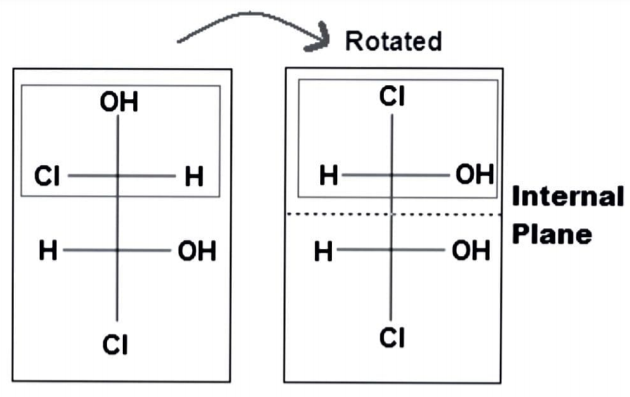
The substituted groups attached to a stereocenter can be rotated around to consider the internal plane, which is an interesting feature of single bonds or $ s{p^3} $ -orbitals. The stereochemistry of the molecule does not shift when it rotates.
Complete answer:
Meso compounds have several chiral centres and are achiral compounds. Despite its stereocenters, it is optically inactive since it is superimposed on its mirror image.A meso compound should have two or more equivalent substituted stereocenters in general. In addition, the compound is divided in half by an internal symmetry plane. The internal mirror reflects the two halves back at each other. Stereocenters' stereochemistry can "cancel out." What this implies is that when a compound is divided into two symmetrical sides by an internal plane, the stereochemistry of the left and right sides should be opposite, resulting in optically inactive results. It's possible that cyclic compounds are also meso.
Let’s see how we can identify meso.
If A is a meso compound, it must have at least two stereocenters, an internal plane, and R and S stereochemistry.
Look for an internal plane, also known as an internal mirror, that runs through the compound.
The stereochemistry (e.g., R or S) is extremely important in deciding whether or not a compound is a meso compound. Since a meso compound is optically inactive, the stereochemistry of the two can balance out. In a meso compound with two stereocenters, for example, R cancels out S.

Note:
The substituted groups attached to a stereocenter can be rotated around to consider the internal plane, which is an interesting feature of single bonds or $ s{p^3} $ -orbitals. The stereochemistry of the molecule does not shift when it rotates.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




