
How does particle movement differ in different states of matter?
Answer
555k+ views
Hint:Matter is something which is around us and occupies space and have mass. We know that there are three major states of matter: solid liquid and gas. These states differ from each other in respect of the position of their molecules.
Complete step-by-step answer:The three states of matter are different forms in which the matter around us exists. These three states of matter can be differentiated from each other based on the movements of their particles.
Let us study in detail the movements of particles in different states of matter.
Solid: A solid’s particles are packed closely together. The forces between the particles are strong enough that the particles cannot move freely, they can only vibrate. As a result, a solid has a stable, definite shape and a definite volume. Therefore, we can say that particles of solids only show vibrational motion at their place ant there is negligible movement.
A diagrammatic representation of molecules of solid is below:
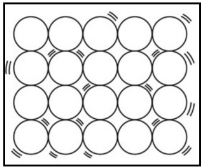
Liquid: In liquids the particles are relatively farther from each other and as a result they can show significant movements. As a result of their movement property, liquids are called fluids. A liquid has a fixed volume but not a fixed shape.
A diagrammatic representation of molecules of liquid:
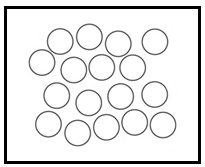
Gas: In gases the molecules are farther apart from each other. In fact, they are very far from each other and hence they have the greatest movement as compared with all the states of matter. Gases have neither fixed shape nor the fixed volume. Gases can easily spread from one corner to another as their particles show greater and faster movement.
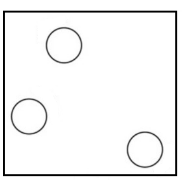
Note: It should be noted that in extreme environments, other states may be present, such as plasma, Bose Einstein condensates and neutron stars. Further states such as quark-gluon plasmas are believed to be possible.
Complete step-by-step answer:The three states of matter are different forms in which the matter around us exists. These three states of matter can be differentiated from each other based on the movements of their particles.
Let us study in detail the movements of particles in different states of matter.
Solid: A solid’s particles are packed closely together. The forces between the particles are strong enough that the particles cannot move freely, they can only vibrate. As a result, a solid has a stable, definite shape and a definite volume. Therefore, we can say that particles of solids only show vibrational motion at their place ant there is negligible movement.
A diagrammatic representation of molecules of solid is below:

Liquid: In liquids the particles are relatively farther from each other and as a result they can show significant movements. As a result of their movement property, liquids are called fluids. A liquid has a fixed volume but not a fixed shape.
A diagrammatic representation of molecules of liquid:

Gas: In gases the molecules are farther apart from each other. In fact, they are very far from each other and hence they have the greatest movement as compared with all the states of matter. Gases have neither fixed shape nor the fixed volume. Gases can easily spread from one corner to another as their particles show greater and faster movement.

Note: It should be noted that in extreme environments, other states may be present, such as plasma, Bose Einstein condensates and neutron stars. Further states such as quark-gluon plasmas are believed to be possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





