
Does the cyanide ion only have one dominant resonance structure? Why?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: The Lewis structures which describe the delocalization of electrons in a polyatomic ion or molecule are known as resonance or canonical structures. It is the best way to describe the combination of several contributing structures into a hybrid structure in valence bond theory for certain ions or molecules.
Complete answer:
We need to use resonance structures when there is a possibility of formation of more than one Lewis structure for a molecule. Some rules to recognize resonance structures are as follows:
1. Atoms never move i.e.; sigma bonds never break in resonating structures.
2. Only $\pi $ electrons or lone pairs which are present in the p orbital are allowed to move in resonance structures.
3. The overall charge of the complete system must remain constant.
Rules for ranking resonance structures are as follows:
1. Octet rule should be followed by each atom within a molecule.
2. Charge separation must be according to electronegativity of the atoms.
3. Formal charges are used to predict resonance structures which are favoured.
Now, in case of cyanide ion, the resonating structures may be represented as follows:
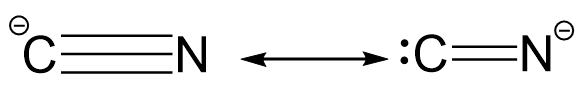
In the first structure, the octet of both carbon as well as nitrogen atom is complete whereas in the second structure, the octet of carbon atom is incomplete which violates the primary rule for resonating structures and thus, it is not a feasible resonating structure.
Hence, the cyanide ion only has one dominant resonance structure because the octet of each atom is complete.
Note:
Remember that the resonating structures are not isomers that means they only differ in position of electrons but not in the position of nucleus. The real structure or hybrid structure of the molecule or ion has comparatively less potential energy than contributing structures.
Complete answer:
We need to use resonance structures when there is a possibility of formation of more than one Lewis structure for a molecule. Some rules to recognize resonance structures are as follows:
1. Atoms never move i.e.; sigma bonds never break in resonating structures.
2. Only $\pi $ electrons or lone pairs which are present in the p orbital are allowed to move in resonance structures.
3. The overall charge of the complete system must remain constant.
Rules for ranking resonance structures are as follows:
1. Octet rule should be followed by each atom within a molecule.
2. Charge separation must be according to electronegativity of the atoms.
3. Formal charges are used to predict resonance structures which are favoured.
Now, in case of cyanide ion, the resonating structures may be represented as follows:

In the first structure, the octet of both carbon as well as nitrogen atom is complete whereas in the second structure, the octet of carbon atom is incomplete which violates the primary rule for resonating structures and thus, it is not a feasible resonating structure.
Hence, the cyanide ion only has one dominant resonance structure because the octet of each atom is complete.
Note:
Remember that the resonating structures are not isomers that means they only differ in position of electrons but not in the position of nucleus. The real structure or hybrid structure of the molecule or ion has comparatively less potential energy than contributing structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




