
What does the distillation of phenol with Zinc Dust result in?
(A) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$
(B) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$
(C) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}$
(D) ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-O-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: A common name for this reaction is the Baeyer reduction of aromatic oxygen-containing compounds. Here, reduction of phenol will occur.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us break this reaction down step-by-step to help facilitate better understanding of the concept.
- Let us now go through the mechanism of this reaction to understand how the formation of Benzene and Zinc Oxide (ZnO) really takes place.
- Zn shows an oxidation state of +2.
- The phenol turns into phenoxide ion and the proton that is released accepts an electron from Zn forming H radical.
- Also because of the heating there is homolytic fission of C of phenyl ring and O-
- Thus, the O-atom formed accepts an electron from Zn and forms oxide ion.
- In this way zinc metal forms zinc oxide and phenyl radical produced here forms a bond with hydrogen radical.
- However, the yield of this reaction is lower.
- The full mechanism is shown step-by-step in the following figure:
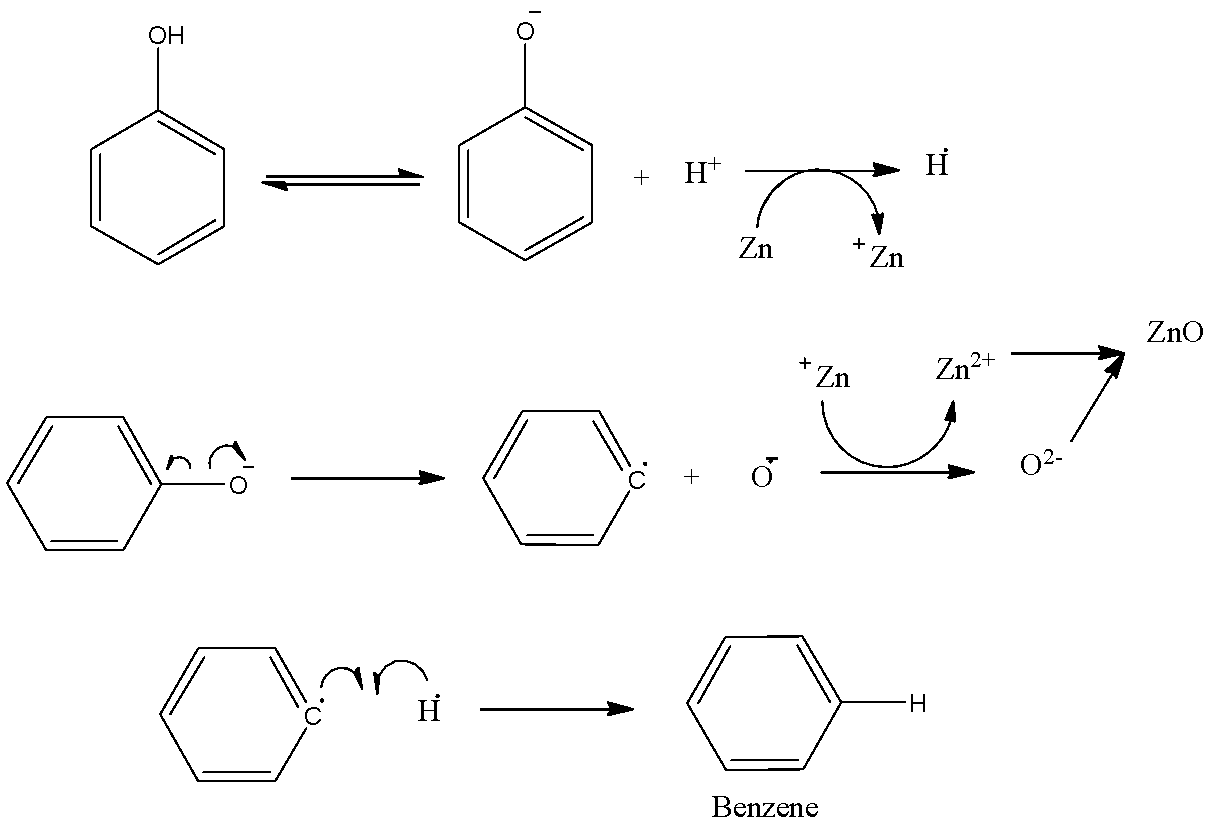
- Observe that the formation of ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{10}}$ and ${{H}_{2}}$ is also possible due to the fusion of the benzene and the hydrogen radicals with another one of the same kinds.
- The equation of the given reaction is as follows:
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-OH\xrightarrow{ZnO}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Do not assume that Zinc oxide will oxidise phenol as it has an oxygen atom in it. Remember that actually it is used as a reducing agent. Remember that Zinc oxide cannot reduce carbon-carbon double bonds. It can only reduce carbon-oxygen single bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us break this reaction down step-by-step to help facilitate better understanding of the concept.
- Let us now go through the mechanism of this reaction to understand how the formation of Benzene and Zinc Oxide (ZnO) really takes place.
- Zn shows an oxidation state of +2.
- The phenol turns into phenoxide ion and the proton that is released accepts an electron from Zn forming H radical.
- Also because of the heating there is homolytic fission of C of phenyl ring and O-
- Thus, the O-atom formed accepts an electron from Zn and forms oxide ion.
- In this way zinc metal forms zinc oxide and phenyl radical produced here forms a bond with hydrogen radical.
- However, the yield of this reaction is lower.
- The full mechanism is shown step-by-step in the following figure:

- Observe that the formation of ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{10}}$ and ${{H}_{2}}$ is also possible due to the fusion of the benzene and the hydrogen radicals with another one of the same kinds.
- The equation of the given reaction is as follows:
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-OH\xrightarrow{ZnO}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Do not assume that Zinc oxide will oxidise phenol as it has an oxygen atom in it. Remember that actually it is used as a reducing agent. Remember that Zinc oxide cannot reduce carbon-carbon double bonds. It can only reduce carbon-oxygen single bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




