
Does the knee-jerk reflex Involve the Brain?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: Reflexes are sudden reactions to any activity mostly physically from the body. When a body undergoes sudden jerk or uncertain movements then the reflexes present in the brain transmits immediate signals for protection through neurons. Hence, the brain is not totally involved in the action. It’s the muscles and neurons combination which responds to the action.
Complete answer:
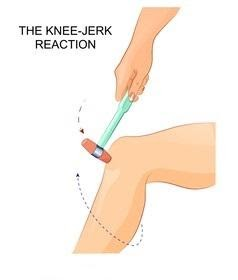
In the knee-jerk reflex there is a tendon present below the knee which causes sudden reflexes. Knee-jerk reflex known as patellar reflex, sudden jerk reflex is determined with kicking or movements of lower leg in response to the kneecap. When the muscles contract and the contraction tends to straighten the leg in kicking motion.
Nerve involvement is also there in jerk reflexes. The nerve involving is land nerve roots. Which exist in the jerk expression with exclusively L radiculopathy. The reflexes in the human body are part of thinking and consciousness so, there is no brain involvement. The sensory signals in our body directs the nerve and a reflex action is being objected.
Instead of brain involvement, the spinal cord is sending signals for control. The knee-jerk reflex includes the contraction of quadriceps muscle. The patellar tendon is stretched and the reflex arc from the spindles to quadriceps to motor neurons which shows the leg movement.
The hit of the knee-jerk is to stretch the muscle and along with sending signals from the sensory neuron to the spinal cord. The knee-jerk reflex is the simple monosynaptic reflex.
Note:
Hence, there is no brain involvement; the jerk reflex of the knee is having no input from the brain. The knee jerk reflex is demonstrated by hitting the patella bone which is located below the knee. Sensors present that part detect the hitting and stretch the tendon from that particular area sending electrical impulses from the spinal cord.
Complete answer:
In the knee-jerk reflex there is a tendon present below the knee which causes sudden reflexes. Knee-jerk reflex known as patellar reflex, sudden jerk reflex is determined with kicking or movements of lower leg in response to the kneecap. When the muscles contract and the contraction tends to straighten the leg in kicking motion.
Nerve involvement is also there in jerk reflexes. The nerve involving is land nerve roots. Which exist in the jerk expression with exclusively L radiculopathy. The reflexes in the human body are part of thinking and consciousness so, there is no brain involvement. The sensory signals in our body directs the nerve and a reflex action is being objected.
Instead of brain involvement, the spinal cord is sending signals for control. The knee-jerk reflex includes the contraction of quadriceps muscle. The patellar tendon is stretched and the reflex arc from the spindles to quadriceps to motor neurons which shows the leg movement.
The hit of the knee-jerk is to stretch the muscle and along with sending signals from the sensory neuron to the spinal cord. The knee-jerk reflex is the simple monosynaptic reflex.

Note:
Hence, there is no brain involvement; the jerk reflex of the knee is having no input from the brain. The knee jerk reflex is demonstrated by hitting the patella bone which is located below the knee. Sensors present that part detect the hitting and stretch the tendon from that particular area sending electrical impulses from the spinal cord.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




