
How many donor atoms are present in EDTA?
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint:
We know that, the full name of EDTA is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and its molecular formula is \[{{\rm{C}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{16}}}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{8}}}\]. It has pH value between \[ - {\rm{0}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{to}}\;{\rm{12}}\]. EDTA is versatile in nature. It can be used in the medical area and industrial area. It behaves as an acid, aminopolycarboxylic acid. It shows many side effects.
Complete step by step solution
Now, let’s discuss EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) in detail.
As we know that EDTA is a chelating agent, which is used in the separation of dye and other substances from heavy metals.it is a type of compound which can be used in household and industrial areas. In European inland, it has the highest concentration that is why it is named as an anthropogenic compound. Studies have detected poor biodegradability in the natural ecosystem. The structure of EDTA is shown below.
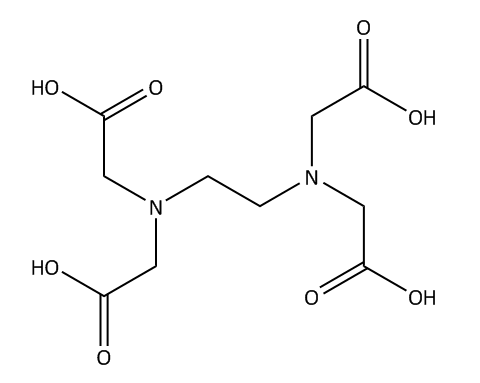
It is a hexadentate ligand, which means it has \[6\] lone pair of electrons that participate in coordination bonding. When a metal reacts with one molecule of EDTA, it can form \[6\] valent coordination complex. Metal ions have \[4\]bonds on oxygen atoms that are negatively charged and \[2\] bonds to a single electron pair on the nitrogen atom.
Therefore, EDTA has six donor atoms.
Notes:
EDTA is used as an anticoagulant for blood as it forms chelate with the calcium ions present in the blood responsible for the coagulation of blood. It is concluded that EDTA acts in the environment as a persistent substance and that its contribution to bioavailability and remobilization of heavy metals.
We know that, the full name of EDTA is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and its molecular formula is \[{{\rm{C}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{16}}}}{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{8}}}\]. It has pH value between \[ - {\rm{0}}{\rm{.8}}\;{\rm{to}}\;{\rm{12}}\]. EDTA is versatile in nature. It can be used in the medical area and industrial area. It behaves as an acid, aminopolycarboxylic acid. It shows many side effects.
Complete step by step solution
Now, let’s discuss EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) in detail.
As we know that EDTA is a chelating agent, which is used in the separation of dye and other substances from heavy metals.it is a type of compound which can be used in household and industrial areas. In European inland, it has the highest concentration that is why it is named as an anthropogenic compound. Studies have detected poor biodegradability in the natural ecosystem. The structure of EDTA is shown below.

It is a hexadentate ligand, which means it has \[6\] lone pair of electrons that participate in coordination bonding. When a metal reacts with one molecule of EDTA, it can form \[6\] valent coordination complex. Metal ions have \[4\]bonds on oxygen atoms that are negatively charged and \[2\] bonds to a single electron pair on the nitrogen atom.
Therefore, EDTA has six donor atoms.
Notes:
EDTA is used as an anticoagulant for blood as it forms chelate with the calcium ions present in the blood responsible for the coagulation of blood. It is concluded that EDTA acts in the environment as a persistent substance and that its contribution to bioavailability and remobilization of heavy metals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




