
Double bond equivalent or degree of unsaturation for the compound given below is?
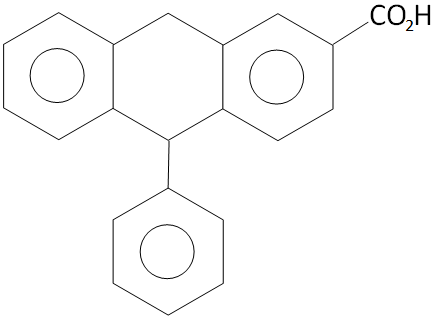
A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 15

Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint- In order to deal with this question first we will define the term degree of unsaturation, then according to the given structure we will calculate the double bond equivalent which directly refers to the degree of unsaturation.
Complete answer:
The degree of unsaturation (also known as the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD), double bond equivalents, or unsaturation index) in the analysis of the molecular formula of organic molecules is a calculation which determines the total number of rings and $\pi $ bonds.
As we know that double bond equivalent is the sum of the total number of rings present in the structure and the total number of double bonds, so Double bond equivalent of the compound = (Number of benzene rings contained + Number of double bonds in the compound).
Here in the given compound, there are 4 rings in which 9 double bond are occupied and 1 double bond is in the structure of functional group
So, the Double bond equivalent $ = 4 + 9 + 1 = 14$
Hence, double bond equivalent or degree of unsaturation for the compound given is 14.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Additional information-
A chemical compound can be considered any substance composed of two or more different types of atoms (atomic elements) in a defined stoichiometric proportion; the term is most readily understood when discussing pure chemical substances. It follows from their being composed of fixed proportions of two or more types of atoms that through chemical reaction, chemical compounds can be divided into compounds or substances each with fewer atoms. The ratio of each product in the compound is represented in a ratio in its chemical formula.
Note- In general, unsaturated compounds undergo standard additional reactions not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes. A saturated organic compound either has single or carbon atomic bonds. The degree of unsaturation shows the total number of pi bonds and rings within a molecule, making it easier for one to determine the molecular structure.
Complete answer:
The degree of unsaturation (also known as the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD), double bond equivalents, or unsaturation index) in the analysis of the molecular formula of organic molecules is a calculation which determines the total number of rings and $\pi $ bonds.
As we know that double bond equivalent is the sum of the total number of rings present in the structure and the total number of double bonds, so Double bond equivalent of the compound = (Number of benzene rings contained + Number of double bonds in the compound).
Here in the given compound, there are 4 rings in which 9 double bond are occupied and 1 double bond is in the structure of functional group
So, the Double bond equivalent $ = 4 + 9 + 1 = 14$
Hence, double bond equivalent or degree of unsaturation for the compound given is 14.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Additional information-
A chemical compound can be considered any substance composed of two or more different types of atoms (atomic elements) in a defined stoichiometric proportion; the term is most readily understood when discussing pure chemical substances. It follows from their being composed of fixed proportions of two or more types of atoms that through chemical reaction, chemical compounds can be divided into compounds or substances each with fewer atoms. The ratio of each product in the compound is represented in a ratio in its chemical formula.
Note- In general, unsaturated compounds undergo standard additional reactions not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes. A saturated organic compound either has single or carbon atomic bonds. The degree of unsaturation shows the total number of pi bonds and rings within a molecule, making it easier for one to determine the molecular structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




