
Draw a clover leaf structure of tRNA showing the following
(i) Tyrosine attached to its amino acid site.
(ii) Anticodon for this amino acid in its correct site (codon for tyrosine is UCA).
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:The tRNA or transfer nucleic acid is a type of RNA or ribose nucleic acid. The tRNA is a short nucleotide chain of RNA. The tRNA plays a major role in decoding the sequence of mRNA or messenger RNA into a protein. The tRNA is three-leaf clover shaped and it has specific folds with three hairpin-like loops attached to it. All tRNAs will have structure after folding containing 4 major stems and 3 major loops.
Complete answer
We have to draw the cloverleaf structure of tRNA and then label anticodon on it. For that we first need to understand the structure of tRNA and the concept of anticodon.
Francis Crick postulated the existence of tRNA. It was also called as soluble RNA (sRNA) before the postulation of genetic code. About 15% of the total cellular RNA constitutes tRNA. The tRNAs are structural molecules. Each tRNA molecule will have two important parts, an anticodon and a specific site for attaching amino acids. The role of specific tRNA is to attach to codons on mRNA template and add the corresponding amino acid in the polypeptide chain. Hence, tRNA are also called translators which actually translate the language of RNA into proteins.
Each tRNA has its corresponding amino acid attached to its end. Tyrosine is a non-polar or hydrophobic α amino acid. It is an aromatic α amino acid, as it contains an aromatic functional group in its structure. The high carbon and hydrogen content in tyrosine is responsible for its hydrophobic nature.
Anticodon is a sequence present on one of the hairpin loops of tRNA. The anticodon can recognize and decode an mRNA codon. At one end of each tRNA it has a loop with three nucleotides of the molecules that can have a base pair with an mRNA molecule. These three nucleotides are termed as anticodon.
The diagram given below shows cloverleaf structure of tRNA with said labelled parts.
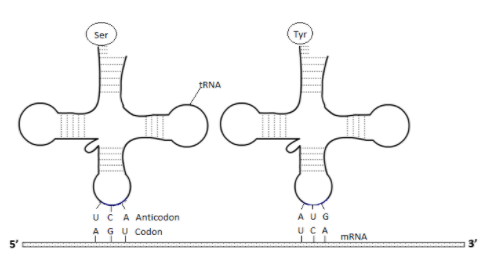
Note:While drawing a clover leaf shaped structure of tRNA, students should keep in mind that it has only three loops. The cloverleaf shaped structure of tRNA is the secondary structure of tRNA. It is basically a simplified version of complex tRNA structure.
Students should keep in mind that they have to draw the codon and anticodon at the end of the cloverleaf structure in one loop. The upper end of the tRNA structure will be without a loop.
Complete answer
We have to draw the cloverleaf structure of tRNA and then label anticodon on it. For that we first need to understand the structure of tRNA and the concept of anticodon.
Francis Crick postulated the existence of tRNA. It was also called as soluble RNA (sRNA) before the postulation of genetic code. About 15% of the total cellular RNA constitutes tRNA. The tRNAs are structural molecules. Each tRNA molecule will have two important parts, an anticodon and a specific site for attaching amino acids. The role of specific tRNA is to attach to codons on mRNA template and add the corresponding amino acid in the polypeptide chain. Hence, tRNA are also called translators which actually translate the language of RNA into proteins.
Each tRNA has its corresponding amino acid attached to its end. Tyrosine is a non-polar or hydrophobic α amino acid. It is an aromatic α amino acid, as it contains an aromatic functional group in its structure. The high carbon and hydrogen content in tyrosine is responsible for its hydrophobic nature.
Anticodon is a sequence present on one of the hairpin loops of tRNA. The anticodon can recognize and decode an mRNA codon. At one end of each tRNA it has a loop with three nucleotides of the molecules that can have a base pair with an mRNA molecule. These three nucleotides are termed as anticodon.
The diagram given below shows cloverleaf structure of tRNA with said labelled parts.

Note:While drawing a clover leaf shaped structure of tRNA, students should keep in mind that it has only three loops. The cloverleaf shaped structure of tRNA is the secondary structure of tRNA. It is basically a simplified version of complex tRNA structure.
Students should keep in mind that they have to draw the codon and anticodon at the end of the cloverleaf structure in one loop. The upper end of the tRNA structure will be without a loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




