
Draw a diagram for this Galvanic cell, labeling the electron flow, the anode and cathode, and the positive and negative sides of the Galvanic cell?
The Galvanic cell runs on the following reaction:
$ Co(s){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}C{u^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}C{o^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}Cu(s) $
Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: The galvanic cell is the common name of an electrochemical cell. Hence we will draw the electrochemical cell having electrodes of cobalt and copper. The oxidation will take place at the cobalt electrode, hence it will act as anode. Reduction will take place at copper electrodes, hence act as cathode. The flow of electric current will be opposite to the flow of electric current.
Complete step by step answer:
The cell which is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy is called an electrochemical cell. Here we will use two electrodes. One will be anode and another will be cathode. At anode oxidation takes place therefore from the given reaction, a cobalt electrode will be used as anode. While at cathode reduction takes place therefore from the given reaction copper electrode will be used as cathode. The reaction will be represented as:
At anode:
$ Co(s){\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}C{o^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ + 2}}e $ ________ $ (i) $
At cathode:
$ C{u^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ + 2e }} \to {\text{ }}Cu(s){\text{ }} $ ________ $ (ii) $
On adding equation $ (i) $ and $ (ii) $ we get the resultant equation as:
$ Co(s){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}C{u^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}C{o^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}Cu(s) $ The diagram for this Galvanic cell is shown below:
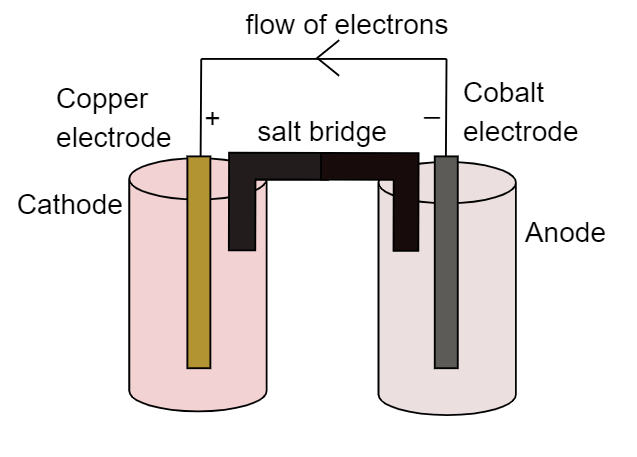
The direction of electron flow will flow from cobalt electrode to copper electrode through an external circuit. Thus the direction of electric current will be in the opposite direction of this flow of electrons.
Note:
It must be noted that anode has greater concentration of electrons because of oxidation and thus electrons from higher concentration anode to lower concentration cathode. The electric current will flow in the opposite direction from cathode to anode and hence cathode is positive and anode is negative. Salt bridges maintain the electrical neutrality between the two mediums. We cannot use direct connections instead of salt bridges because electrical neutrality cannot be maintained.
Complete step by step answer:
The cell which is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy is called an electrochemical cell. Here we will use two electrodes. One will be anode and another will be cathode. At anode oxidation takes place therefore from the given reaction, a cobalt electrode will be used as anode. While at cathode reduction takes place therefore from the given reaction copper electrode will be used as cathode. The reaction will be represented as:
At anode:
$ Co(s){\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}C{o^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ + 2}}e $ ________ $ (i) $
At cathode:
$ C{u^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ + 2e }} \to {\text{ }}Cu(s){\text{ }} $ ________ $ (ii) $
On adding equation $ (i) $ and $ (ii) $ we get the resultant equation as:
$ Co(s){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}C{u^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}C{o^{2 + }}(aq.){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}Cu(s) $ The diagram for this Galvanic cell is shown below:

The direction of electron flow will flow from cobalt electrode to copper electrode through an external circuit. Thus the direction of electric current will be in the opposite direction of this flow of electrons.
Note:
It must be noted that anode has greater concentration of electrons because of oxidation and thus electrons from higher concentration anode to lower concentration cathode. The electric current will flow in the opposite direction from cathode to anode and hence cathode is positive and anode is negative. Salt bridges maintain the electrical neutrality between the two mediums. We cannot use direct connections instead of salt bridges because electrical neutrality cannot be maintained.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




