
Draw a diagram to describe the life cycle of the moss, pointing out significant features.
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: They belong to the amphibians of the plant kingdoms and also show the alternation of generation in their life cycle.
Complete answer:
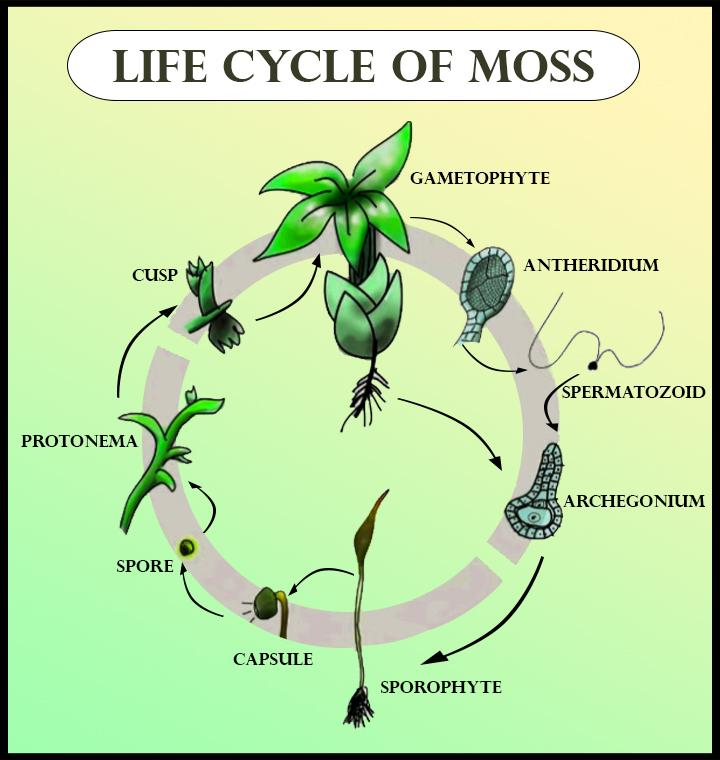
Mosses belong to the division Bryophyta. They are the small, non-vascular plants that are flowerless. They are autotrophic as they undergo photosynthesis. The life cycle of mosses shows alternation of generation. They consist of only a single set of haploid chromosomes. The period when the moss plant has two paired chromosomes is known as the sporophyte stage.
The life cycle starts with the sore, which is haploid and resulting in the production of protonema. Protonema is the thallus-like, flat thread-like filaments. From this stage, gametophore grows, which later forms stems and leaves. The gametophore is the gamete bearers.
From the tips of the gametophore stems, the sex organs are developed. The female organs are known as archegonia (small, flask-shaped cells with an open neck, and male organs are known as antheridia (sperm). In the water, sperm swim towards archegonia, and fertilization occurs. The pollination occurs mainly through the wind.
After fertilization, the immature sporophyte pushed out of the archegonial venter and developed into the mature sporophyte. They consisted of seta (long stalk), and a capsule capped cell called an operculum. In the capsule during meiosis, spore formation occurs and forms haploid spores. After this, the new cycle begins.
Note: Mosses were generally grouped with the hornworts and liverworts. The fossil fuel of moss is studied that they recovered from early Permian later in the Carboniferous and Silurian period. They evolved only about two to three times much slower than ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
Complete answer:
Mosses belong to the division Bryophyta. They are the small, non-vascular plants that are flowerless. They are autotrophic as they undergo photosynthesis. The life cycle of mosses shows alternation of generation. They consist of only a single set of haploid chromosomes. The period when the moss plant has two paired chromosomes is known as the sporophyte stage.
The life cycle starts with the sore, which is haploid and resulting in the production of protonema. Protonema is the thallus-like, flat thread-like filaments. From this stage, gametophore grows, which later forms stems and leaves. The gametophore is the gamete bearers.
From the tips of the gametophore stems, the sex organs are developed. The female organs are known as archegonia (small, flask-shaped cells with an open neck, and male organs are known as antheridia (sperm). In the water, sperm swim towards archegonia, and fertilization occurs. The pollination occurs mainly through the wind.
After fertilization, the immature sporophyte pushed out of the archegonial venter and developed into the mature sporophyte. They consisted of seta (long stalk), and a capsule capped cell called an operculum. In the capsule during meiosis, spore formation occurs and forms haploid spores. After this, the new cycle begins.

Note: Mosses were generally grouped with the hornworts and liverworts. The fossil fuel of moss is studied that they recovered from early Permian later in the Carboniferous and Silurian period. They evolved only about two to three times much slower than ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




