
Draw a Graafian follicle and label antrum and secondary oocyte.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: Before ovulation, a follicular stage after the first meiotic division is present which is known as the Graafian follicle. It contains a 2N haploid oocyte. It is characterized by the large follicular antrum which makes up most of the follicle. The secondary oocyte is located eccentrically.
Complete answer:
Graafian follicles are the ovarian follicles that are rounded enclosures for developing ova in the cortex near the surface of the ovary. At birth and in childhood they are present as numerous undeveloped or primary ovarian follicles. Each contains an oocyte or primitive ovum, and each one is covered by a single layer of flattened cells. A young female has as many as 700,000 primary follicles contained in the two ovaries. Most of these degenerate before or after puberty.
During the foetus development, many oogonia are produced and undergo mitosis to form primary oocytes and they remain at prophase of meiosis I throughout the childhood. Primary oocytes are enclosed by a single layer of cells called granulosa cells and form structures known as the primordial follicles. As the granulosa cells multiply and form many layers of cells around the primary oocyte, the primordial follicle first becomes the primary follicle. In addition to this, the cells from stroma of the ovary form further layers of granulosa cells and the theca and collectively called as secondary follicles. A fluid is secreted by granulosa cells that contain the hormone oestrogen, as the secondary follicle develops. A fluid –filled cavity or space called the antrum, develops in the follicle and it is now called a tertiary follicle. Oestrogen stimulates the growth of follicle, which eventually becomes a mature follicle known as the Graafian follicle.
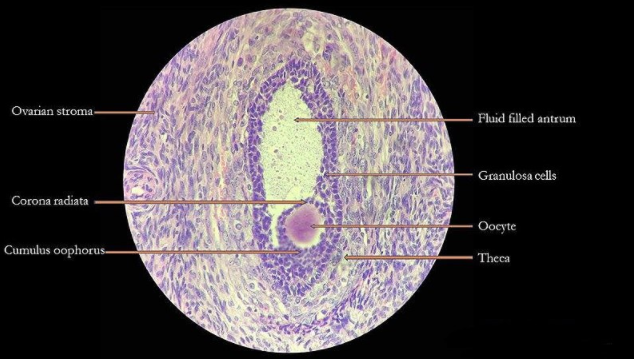
Note: The ovarian follicle has two functions. It provides for the release and maturation of a fertilized oocyte. It forms the corpus luteum, which maintains and promotes the implantation of the embryo.
Complete answer:
Graafian follicles are the ovarian follicles that are rounded enclosures for developing ova in the cortex near the surface of the ovary. At birth and in childhood they are present as numerous undeveloped or primary ovarian follicles. Each contains an oocyte or primitive ovum, and each one is covered by a single layer of flattened cells. A young female has as many as 700,000 primary follicles contained in the two ovaries. Most of these degenerate before or after puberty.
During the foetus development, many oogonia are produced and undergo mitosis to form primary oocytes and they remain at prophase of meiosis I throughout the childhood. Primary oocytes are enclosed by a single layer of cells called granulosa cells and form structures known as the primordial follicles. As the granulosa cells multiply and form many layers of cells around the primary oocyte, the primordial follicle first becomes the primary follicle. In addition to this, the cells from stroma of the ovary form further layers of granulosa cells and the theca and collectively called as secondary follicles. A fluid is secreted by granulosa cells that contain the hormone oestrogen, as the secondary follicle develops. A fluid –filled cavity or space called the antrum, develops in the follicle and it is now called a tertiary follicle. Oestrogen stimulates the growth of follicle, which eventually becomes a mature follicle known as the Graafian follicle.

Note: The ovarian follicle has two functions. It provides for the release and maturation of a fertilized oocyte. It forms the corpus luteum, which maintains and promotes the implantation of the embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




