
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer and explain its working. What is the function of the radial magnetic field inside the coil?
Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint :Moving coil galvanometer is known as a device that can be used basically to measure or detect small electric current.. Here, we discuss the principle and construction of the moving coil galvanometer. A radial magnetic field that is produced by cylindrical poles of permanent magnet of galvanometer is always parallel to the plane of the coil.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Moving coil galvanometer (MCG) is basically a device that is used to measure or detect small electric current flowing in the electric circuit.
CONSTRUCTION:
A moving coil galvanometer is a device that contains a coil wound on a non-metallic frame. The coil is suspended between two poles of a permanent magnet that are cylindrical in shape. The coil of MCG is suspended with a movable tension head H by a strip or wire made of phosphor bronze that acts as a path for the current to the coil also. End of the wire is placed and is connected to the terminal ${T_2} $ of the galvanometer. The other end of the coil is connected to a light spring which is finally connected to the terminal ${T_1} $ . The spring exerts a small restoring torque on the coil. The diagram of moving coil galvanometer is shown below
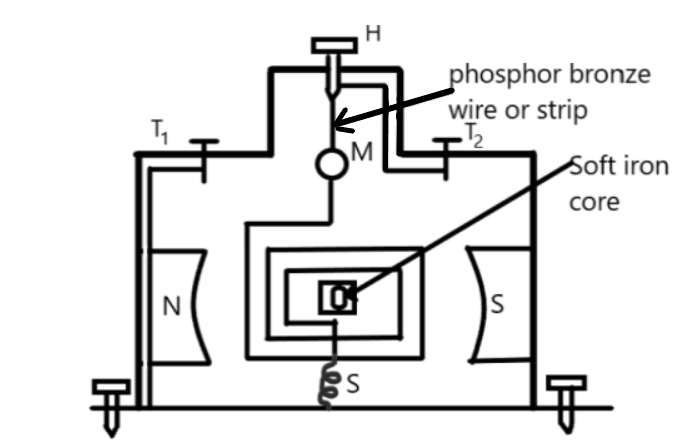
The whole system of the moving coil galvanometer is enclosed in a non-metallic case (say wooden) case to avoid disturbance due to air.
The torque experienced by the coil, when the current flows through the coil, is given by
$\tau = NIAB\sin \theta $
Here, $ $B $ $ is the intensity of the magnetic field, $I $ is the current flowing through the coil, $A $ is the area of the coil, $N $ is the number of turns in the coil. Also, $\theta $ is the angle made by the normal to the plane of the coil with the direction of the magnetic field.
USE OF A RADIAL MAGNETIC FIELD IN THE MOVING COIL GALVANOMETER:
A radial magnetic field that is produced by the cylindrical poles of the permanent magnet of the galvanometer is always parallel to the plane of the coil. Torque produced in the coil of the galvanometer is given by, $\tau = NIAB\sin \theta $ throughout the rotation of the coil.
For a radial magnetic field, the angle between the normal to the plane of the loop and the magnetic field is $90^\circ $ .
$\therefore \,\,\tau = NIAB $
$ \Rightarrow \,\tau \propto I $
Note :
When we use a radial magnetic field, the deflection of the coil will be proportional to the current flowing through the coil. Therefore, we will get a linear scale that can be used to determine the deflection of the coil. Also, for the equilibrium of the coil, deflection of the coil is equal to the restoring torque.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Moving coil galvanometer (MCG) is basically a device that is used to measure or detect small electric current flowing in the electric circuit.
CONSTRUCTION:
A moving coil galvanometer is a device that contains a coil wound on a non-metallic frame. The coil is suspended between two poles of a permanent magnet that are cylindrical in shape. The coil of MCG is suspended with a movable tension head H by a strip or wire made of phosphor bronze that acts as a path for the current to the coil also. End of the wire is placed and is connected to the terminal ${T_2} $ of the galvanometer. The other end of the coil is connected to a light spring which is finally connected to the terminal ${T_1} $ . The spring exerts a small restoring torque on the coil. The diagram of moving coil galvanometer is shown below

The whole system of the moving coil galvanometer is enclosed in a non-metallic case (say wooden) case to avoid disturbance due to air.
The torque experienced by the coil, when the current flows through the coil, is given by
$\tau = NIAB\sin \theta $
Here, $ $B $ $ is the intensity of the magnetic field, $I $ is the current flowing through the coil, $A $ is the area of the coil, $N $ is the number of turns in the coil. Also, $\theta $ is the angle made by the normal to the plane of the coil with the direction of the magnetic field.
USE OF A RADIAL MAGNETIC FIELD IN THE MOVING COIL GALVANOMETER:
A radial magnetic field that is produced by the cylindrical poles of the permanent magnet of the galvanometer is always parallel to the plane of the coil. Torque produced in the coil of the galvanometer is given by, $\tau = NIAB\sin \theta $ throughout the rotation of the coil.
For a radial magnetic field, the angle between the normal to the plane of the loop and the magnetic field is $90^\circ $ .
$\therefore \,\,\tau = NIAB $
$ \Rightarrow \,\tau \propto I $
Note :
When we use a radial magnetic field, the deflection of the coil will be proportional to the current flowing through the coil. Therefore, we will get a linear scale that can be used to determine the deflection of the coil. Also, for the equilibrium of the coil, deflection of the coil is equal to the restoring torque.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




