
Draw a labelled diagram of a myelinated neuron.
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: A neuron, also known as a nerve cell, is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via synapses, which are specialized intercellular connections. Except for sponges and placozoa, it is the major component of nerve tissue in all animals. Nerve cells do not exist in plants or fungi. The neuron is the brain's fundamental functioning unit, a specialized cell that transmits information to other nerve cells, muscle cells, and gland cells. Neurons are nerve cells that send information to other neuron cells, muscle cells, and gland cells.
Complete explanation:
Myelin is a lipid-rich (fatty) material that surrounds nerve cell axons to insulate them and speed up the transmission of electrical impulses. The myelinated axon is similar to an electrical wire that is surrounded by insulating material.
A neuron with a coating of Schwann cell membranes around the axon (sheath).
For quicker action potential conduction, the myelin coating that surrounds the nerve cell is necessary. The peripheral nervous system (particularly sensory and motor neurons) and the white matter of the central nervous system contain this type of neuron.
Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers are nerve fibres without a myelin sheath, whereas myelinated Nerve Fibers have a myelin coat.
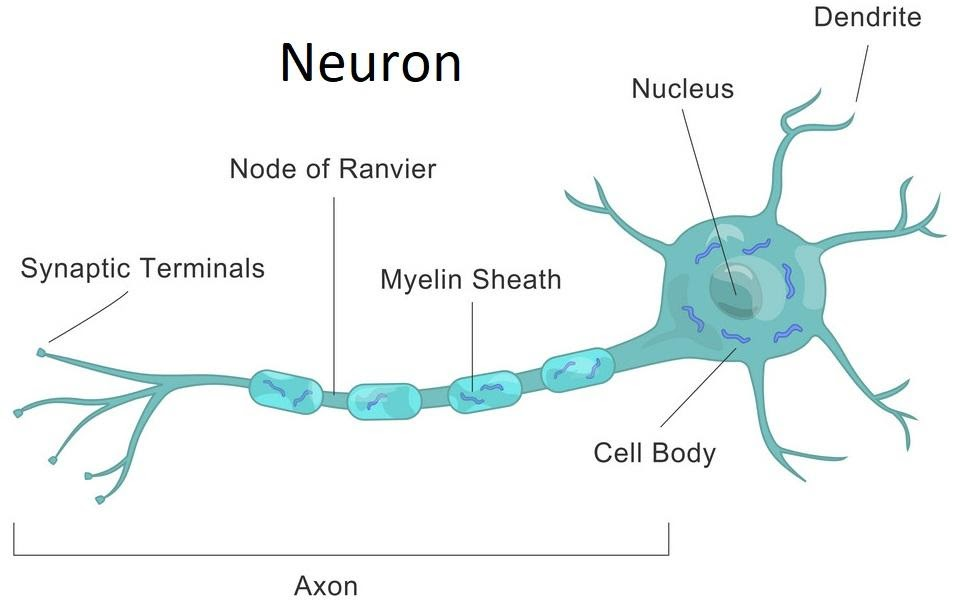
Structure of a myelinated neuron
Note:
A neuron with myelinated axons can conduct the impulse at a quicker rate because the myelin sheath functions as an insulator, allowing the electrical signal to propagate more quickly. Because rapid conduction speeds are required, the majority of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems are myelinated. Because it insulates the axon and assembles voltage-gated sodium channel clusters at distinct nodes along its length, myelin can dramatically improve the speed of electrical impulses in neurons.
Complete explanation:
Myelin is a lipid-rich (fatty) material that surrounds nerve cell axons to insulate them and speed up the transmission of electrical impulses. The myelinated axon is similar to an electrical wire that is surrounded by insulating material.
A neuron with a coating of Schwann cell membranes around the axon (sheath).
For quicker action potential conduction, the myelin coating that surrounds the nerve cell is necessary. The peripheral nervous system (particularly sensory and motor neurons) and the white matter of the central nervous system contain this type of neuron.
Unmyelinated Nerve Fibers are nerve fibres without a myelin sheath, whereas myelinated Nerve Fibers have a myelin coat.

Structure of a myelinated neuron
Note:
A neuron with myelinated axons can conduct the impulse at a quicker rate because the myelin sheath functions as an insulator, allowing the electrical signal to propagate more quickly. Because rapid conduction speeds are required, the majority of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems are myelinated. Because it insulates the axon and assembles voltage-gated sodium channel clusters at distinct nodes along its length, myelin can dramatically improve the speed of electrical impulses in neurons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




