
Draw a labelled diagram of dialysis method, for purification of colloidal solutions.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Dialysis is a purification method for the purification of colloidal solutions. Dialysis is used as a biomedical application for the purification of blood when the kidneys of a person stop proper functioning.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows the labelled diagram for the dialysis method.
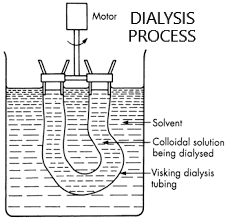
Dialysis is a separation method of electrolytes from colloidal solution, therefore it is used for the purification of colloidal solutions. First of all let us understand what a colloidal solution means.
A colloidal solution is a solution in which the large size particles are suspended in a fluid medium. The suspended particles are called the dispersion phase and the medium is called the dispersion medium. The dispersion phase and medium need not be always solid in liquid but gas in liquid (aerosol), gas in gas, solid in gas, liquid in liquid (emulsion) etc., types also occur.
The colloidal solutions are purified by several different types such as dialysis, electro dialysis, ultrafiltration, electro decantation etc. Dialysis is done by two separate solutions which are separated by a porous membrane called a parchment membrane. When blood for example, is placed in a dialysis tube and inserted into the solvent, water contained in a beaker, the dialysis membrane or parchment membrane allows the unwanted waste materials to flow through it into the water. The membrane does not allow the colloidal particles such as blood cells to pass through it as they are of large size compared to the inorganic salts. Thus blood as a colloidal solution can be artificially filtered to get rid of unwanted substances.
Note: Blood is an excellent example of solid in liquid phase type of natural colloidal solution and it is naturally filtered by kidney to get rid of harmful urea$\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CON}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ and other excess salts. But when the functioning of the kidney fails, the dialysis process is employed bio-medically.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure below shows the labelled diagram for the dialysis method.

Dialysis is a separation method of electrolytes from colloidal solution, therefore it is used for the purification of colloidal solutions. First of all let us understand what a colloidal solution means.
A colloidal solution is a solution in which the large size particles are suspended in a fluid medium. The suspended particles are called the dispersion phase and the medium is called the dispersion medium. The dispersion phase and medium need not be always solid in liquid but gas in liquid (aerosol), gas in gas, solid in gas, liquid in liquid (emulsion) etc., types also occur.
The colloidal solutions are purified by several different types such as dialysis, electro dialysis, ultrafiltration, electro decantation etc. Dialysis is done by two separate solutions which are separated by a porous membrane called a parchment membrane. When blood for example, is placed in a dialysis tube and inserted into the solvent, water contained in a beaker, the dialysis membrane or parchment membrane allows the unwanted waste materials to flow through it into the water. The membrane does not allow the colloidal particles such as blood cells to pass through it as they are of large size compared to the inorganic salts. Thus blood as a colloidal solution can be artificially filtered to get rid of unwanted substances.
Note: Blood is an excellent example of solid in liquid phase type of natural colloidal solution and it is naturally filtered by kidney to get rid of harmful urea$\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CON}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ and other excess salts. But when the functioning of the kidney fails, the dialysis process is employed bio-medically.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




