
Draw a labelled diagram of Ruminant stomach
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:Ruminant stomachs are found in animals called ruminants like cows and deer. They have specially evolved to enable the animals to effectively digest grasses and other vegetation which is difficult for other animals.
Complete answer:
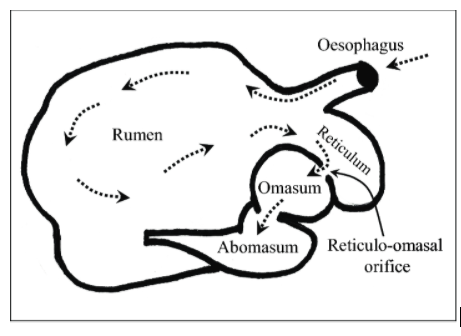
A ruminant’s stomach is divided into four compartments. These are the rumen, the reticulum, obesum, and abomasum. Each compartment is designed to assist a particular stage of digestion.
The largest section of the stomach is the rumen and serves as a storage area for the food. This is also the location where breakdown of cellulose fermentation takes place. Fermentation is assisted by specialised microbes present in the rumen that break down the food to release fatty acids which are then absorbed by the cow’s stomach into the bloodstream. The surface area is made greater by villi like projections called papillae.
The reticulum is the part of the stomach that lies towards the heart of the animal. It is much smaller in size than the rumen and most of the heavier feed passes into this chamber. The two are spoken of as one unit: the reticulorumen.
Food that is softened within the reticulorumen is regurgitated as cud, chewed again and swallowed. Of this the liquid portion enters the omasum, and the remaining matter goes to the abomasum. The omasum is where all the fluid nutrients are absorbed. The abomasum contains gastric acids and enzymes similar to our stomachs.
Note:Ruminants are able to digest cellulose not because they produce cellulose themselves, but due to the presence of cellulose secreting bacteria in the rumen. These kinds of bacteria are also found in the stomachs of termites, which chew wood.
Complete answer:
A ruminant’s stomach is divided into four compartments. These are the rumen, the reticulum, obesum, and abomasum. Each compartment is designed to assist a particular stage of digestion.
The largest section of the stomach is the rumen and serves as a storage area for the food. This is also the location where breakdown of cellulose fermentation takes place. Fermentation is assisted by specialised microbes present in the rumen that break down the food to release fatty acids which are then absorbed by the cow’s stomach into the bloodstream. The surface area is made greater by villi like projections called papillae.
The reticulum is the part of the stomach that lies towards the heart of the animal. It is much smaller in size than the rumen and most of the heavier feed passes into this chamber. The two are spoken of as one unit: the reticulorumen.
Food that is softened within the reticulorumen is regurgitated as cud, chewed again and swallowed. Of this the liquid portion enters the omasum, and the remaining matter goes to the abomasum. The omasum is where all the fluid nutrients are absorbed. The abomasum contains gastric acids and enzymes similar to our stomachs.

Note:Ruminants are able to digest cellulose not because they produce cellulose themselves, but due to the presence of cellulose secreting bacteria in the rumen. These kinds of bacteria are also found in the stomachs of termites, which chew wood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




