
Draw a labelled diagram of T.S of dicot root . Give four differences between the internal structure of dicot and monocot roots.
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: There is a further division of all vascular plants into Monocot and Dicots. This classification is primarily based on the number of cotyledon species. Cotyledons are defined in botany as an essential part of the embryo, a part of a seed. The word cotyledons id was derived from an embryonic leaf, a Greek word. Two distinct kinds of cotyledon are monocotyledons and dicotyledons.
Complete answer:
Internal structure of dicot root:
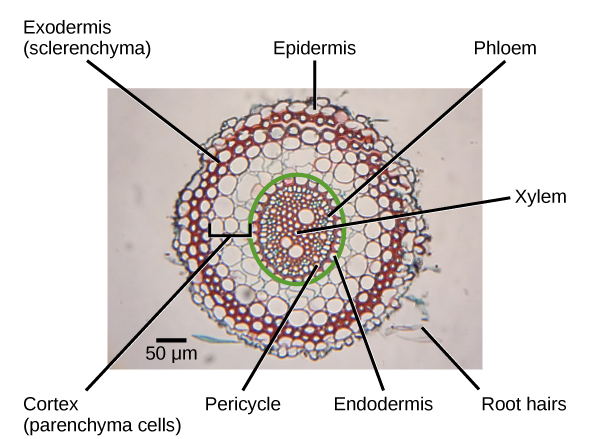
Epidermis:
It is single-layered and made of cells that are thin-walled. There is no cutinisation of the outer walls of epidermal cells. Many epidermal cells, the traditional unicellular hairs of the roots, extend to form long hairy bodies. Root epidermis is sometimes referred to as epiblema or piliferous layer
Cortex:
In terms of roots, it is very broad and extensive. Cortex is made from leucoplast, thin-walled living parenchymal cells that turn sugar into starch grains. The last cortical layer is the endodermis. It is a natural occurrence in the roots.
One layer of barrel-shaped cells is composed of endodermis, which are tightly organized without having intercellular spaces. There are thickened radial walls in the endodermal cells, which are called Casparian strips, after the name of the gentleman who first noted them, Caspary.
Central Cylinder or Stele:
Next to the endodermis is a single-layered pericycle formed by thin-walled parenchyma cells. The Pericycle is the seat of origin of the lateral roots.Vascular bundles in the roots are usually radial. Xylem and phloem form distinct patches and non-conducting cells intervene in them. The number of bundles in dicotyledonous roots is reduced.
Conjunctive tissue:
The conjunctive tissue is produced by thin-walled parenchymatous cells lying between xylem and phloem groups.
Pith:
A tiny parenchymal pith is in the middle. In dicotyledonous roots, it may also be absent.
Note: Xylem is exarch, i.e. protoxylem lies to the periphery and Metaxylem to the middle in monocot and dicot origin.
Endodermis consists of barrel-shaped parenchyma without intercellular spaces in both the dicot and monocot roots.
In both monocot and dicot roots, pith consists of intercellular spaces of thin walled, polygonal parenchyma cells.
There are radial vascular bundles of both monocot and dicot roots
Complete answer:
Internal structure of dicot root:
Epidermis:
It is single-layered and made of cells that are thin-walled. There is no cutinisation of the outer walls of epidermal cells. Many epidermal cells, the traditional unicellular hairs of the roots, extend to form long hairy bodies. Root epidermis is sometimes referred to as epiblema or piliferous layer
Cortex:
In terms of roots, it is very broad and extensive. Cortex is made from leucoplast, thin-walled living parenchymal cells that turn sugar into starch grains. The last cortical layer is the endodermis. It is a natural occurrence in the roots.
One layer of barrel-shaped cells is composed of endodermis, which are tightly organized without having intercellular spaces. There are thickened radial walls in the endodermal cells, which are called Casparian strips, after the name of the gentleman who first noted them, Caspary.
Central Cylinder or Stele:
Next to the endodermis is a single-layered pericycle formed by thin-walled parenchyma cells. The Pericycle is the seat of origin of the lateral roots.Vascular bundles in the roots are usually radial. Xylem and phloem form distinct patches and non-conducting cells intervene in them. The number of bundles in dicotyledonous roots is reduced.
Conjunctive tissue:
The conjunctive tissue is produced by thin-walled parenchymatous cells lying between xylem and phloem groups.
Pith:
A tiny parenchymal pith is in the middle. In dicotyledonous roots, it may also be absent.
| Monocot root | Dicot root | |
| Cortex Pericycle BicycleIn monocot roots, the | With external dead exoderma, the cortex can be heterogeneous (differentiated). | Without any distinction, the cortex is homogeneous. |
| pericycle | only produces the lateral roots. | The pericycle produces the lateral roots, the cork cambium and the vascular cambium portion. |
| Pith | Pith is a big, well formed monocot root component. It contains a significant number of starch grains. | Pith is very tiny or totally obliterated. |
| Xylem andPhloem | In number, Xylem and Phloem are various. | The numbers of Xylem and Phloem are limited. |
| Passage cells | Passage cells are typically absent in monocot root endodermis. | In the endodermis of dicot roots, normally passage cells are present. |
| Metaxylem | Elements are oval or circular | Elements are angular arranged in linear position |

Note: Xylem is exarch, i.e. protoxylem lies to the periphery and Metaxylem to the middle in monocot and dicot origin.
Endodermis consists of barrel-shaped parenchyma without intercellular spaces in both the dicot and monocot roots.
In both monocot and dicot roots, pith consists of intercellular spaces of thin walled, polygonal parenchyma cells.
There are radial vascular bundles of both monocot and dicot roots
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




