
Draw a labelled ray diagram of a reflecting telescope. Mention its two advantages over the refracting telescope.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Reflecting telescope is one that was constructed by Newton. This telescope as the name suggests uses the principle of reflection also, so must consist of a reflecting mirror. Students must draw a well labeled clear diagram for the telescope and then explain its working firstly. Afterward, compare it with other refracting telescopes.
Complete answer:
A telescope is an optical instrument designed to see distant objects, as it makes them appear nearer. It is constructed using an arrangement of lenses, or of curved mirrors and lenses, using these the rays of light are collected and focused and the resulting image is magnified in nature.
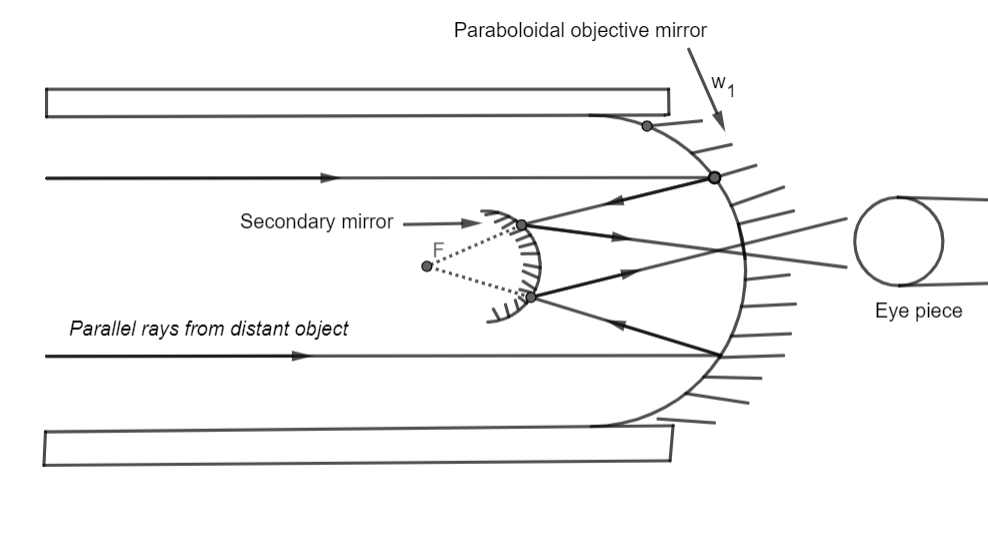
In 1668, the first reflecting telescope was constructed by Newton. It consists of a large paraboloidal (primary) concave mirror of a large focal length with a hole at its center. There is a small convex (secondary mirror) near the focus of the primary mirror. The eyepiece is placed on the axis of the telescope near the hole of the primary mirror.
The following diagram will clearly portray a reflecting telescope:
Let ${f_ \circ }$ be the focal length of the objective and ${f_e}$ the focal length of the eyepiece.
For the final image formed at the least distance of distinct vision:
$m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{f_e}}}{D}} \right)$
For the final image formed at infinity:
$m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{R}{2}}}{{{f_e}}}$.
The following are two advantages of a reflecting telescope in comparison to a refracting telescope:
(i) A concave mirror of a large aperture has a high gathering power and absorbs a very less amount of light than the lenses of a large aperture. Thus the final image formed in the reflecting telescope is very bright. So even the faint or distant stars can be viewed easily.
(ii) The use of a paraboloidal mirror reduces the spherical aberration i.e., the phenomenon of formation of a non-point and blurred image of a point object.
Note: A lot of times it is observed that while drawing ray diagrams students tend to double line a single ray due to frequent erasing and redrawing. Avoid overwriting. Make sure the diagram is clear with all its relevant parts. Label the parts correctly as well.
Another few advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope:
- A mirror requires grinding and polishing of one of its surfaces only. Thus it reduces the cost of constructing a reflecting telescope over a refracting one.
- In refracting telescopes lenses are used which can cause chromatic aberration i.e., the formation of a colored image of a white object, which is not possible in reflecting telescopes as a mirror is used.
- Due to the usage of a high aperture mirror in reflecting telescopes, they have a very high-resolution power.
Complete answer:
A telescope is an optical instrument designed to see distant objects, as it makes them appear nearer. It is constructed using an arrangement of lenses, or of curved mirrors and lenses, using these the rays of light are collected and focused and the resulting image is magnified in nature.
In 1668, the first reflecting telescope was constructed by Newton. It consists of a large paraboloidal (primary) concave mirror of a large focal length with a hole at its center. There is a small convex (secondary mirror) near the focus of the primary mirror. The eyepiece is placed on the axis of the telescope near the hole of the primary mirror.
The following diagram will clearly portray a reflecting telescope:

Let ${f_ \circ }$ be the focal length of the objective and ${f_e}$ the focal length of the eyepiece.
For the final image formed at the least distance of distinct vision:
$m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{f_e}}}{D}} \right)$
For the final image formed at infinity:
$m = \dfrac{{{f_ \circ }}}{{{f_e}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{R}{2}}}{{{f_e}}}$.
The following are two advantages of a reflecting telescope in comparison to a refracting telescope:
(i) A concave mirror of a large aperture has a high gathering power and absorbs a very less amount of light than the lenses of a large aperture. Thus the final image formed in the reflecting telescope is very bright. So even the faint or distant stars can be viewed easily.
(ii) The use of a paraboloidal mirror reduces the spherical aberration i.e., the phenomenon of formation of a non-point and blurred image of a point object.
Note: A lot of times it is observed that while drawing ray diagrams students tend to double line a single ray due to frequent erasing and redrawing. Avoid overwriting. Make sure the diagram is clear with all its relevant parts. Label the parts correctly as well.
Another few advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope:
- A mirror requires grinding and polishing of one of its surfaces only. Thus it reduces the cost of constructing a reflecting telescope over a refracting one.
- In refracting telescopes lenses are used which can cause chromatic aberration i.e., the formation of a colored image of a white object, which is not possible in reflecting telescopes as a mirror is used.
- Due to the usage of a high aperture mirror in reflecting telescopes, they have a very high-resolution power.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




