
Draw a labelled schematic sketch of replication fork of DNA. Explain the role of enzymes involved in DNA replication.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: A replication fork is a structure that is formed during DNA replication within the long helical, double-stranded DNA. Helicases create it by breaking the hydrogen bonds and holding the two DNA strands together in the helix. The resulting structure has two branchings known as prongs. Each prong is made up of a single strand of DNA.
Complete step by step answer:
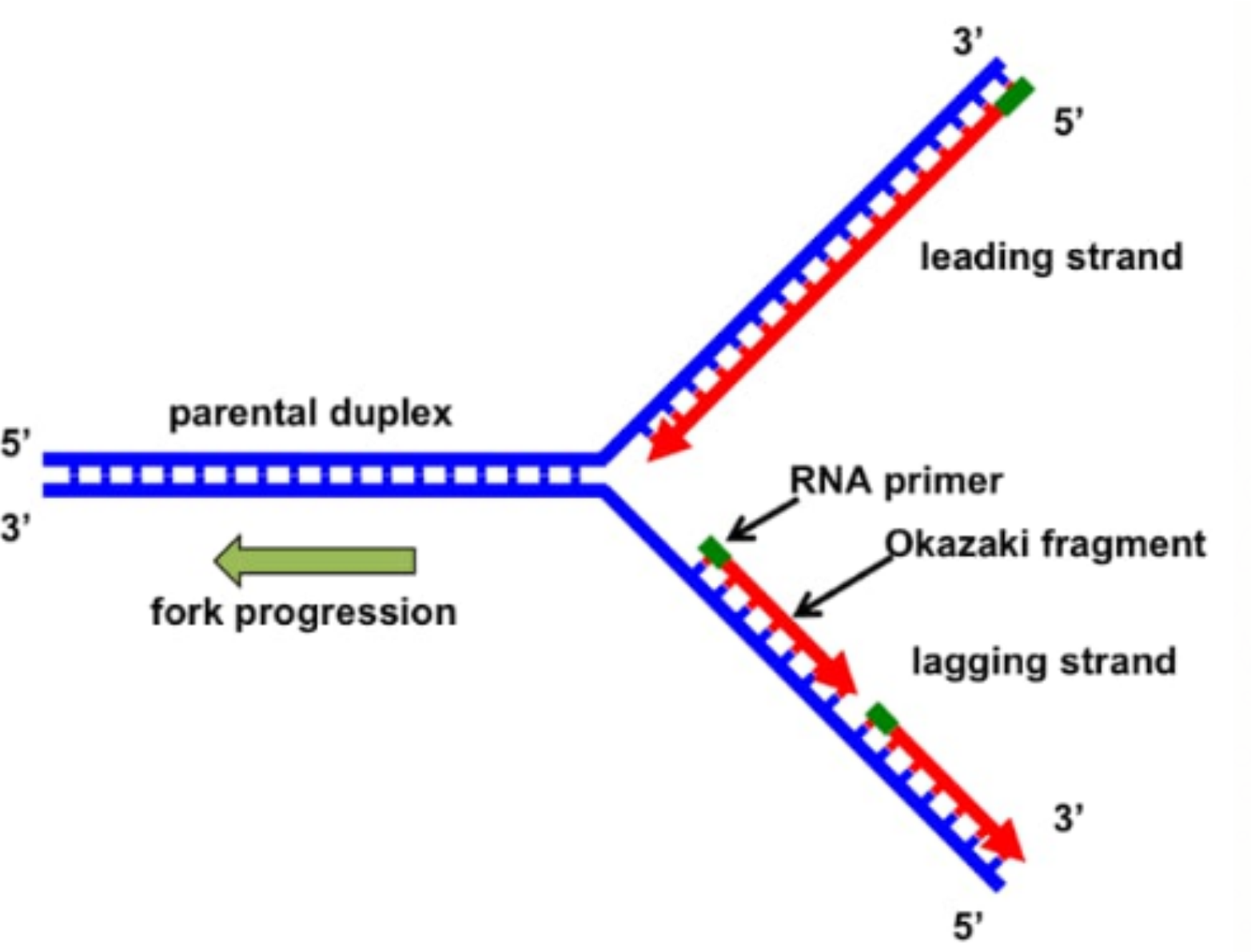
Note: The DNA polymerase can synthesize in one direction only. It works by extending the 3' end of the pre-existing nucleotide chain. Therefore, DNA polymerase moves in 3' - 5' direction along the template strand, and the daughter strand is formed in 5' - 3' direction.
Complete step by step answer:

| Enzyme | Function in DNA replication |
| DNA helicase | It is also called helix destabilizing enzyme. Helicase is responsible for the separation of the two strands of DNA at the replication fork behind topoisomerase. |
| DNA polymerase | This enzyme is responsible for the catalysis of the addition of nucleotides to DNA in 5′ to 3′ direction during the process of DNA replication. It also performs proof-reading and does error correction. There are many types of DNA Polymerase which perform different functions in different types of cells. |
| DNA clamp | It is a protein which prevents the elongation of DNA polymerases to prevent it from dissociating from the parent DNA strand. |
| Single-strand DNA-binding protein | ssDNA binds to the prongs and prevents the DNA double helix from re-annealing after the unwinding with the help of DNA helicase. It maintains the strand separation and facilitates the synthesis of the nascent strand. |
| Topoisomerase | It relaxes the stress in the DNA due to its super-coiled nature. |
| DNA gyrase | It relieves the strain of unwinding by DNA helicase. This is majorly a specific type of topoisomerase |
| DNA ligase | It joins Okazaki Fragments of the lagging strand and re-anneals the semi-conservative strands. |
| Primase | It provides a beginning point of RNA or DNA for the DNA polymerase to start the synthesis of a new DNA strand. |
| Telomerase | It adds repetitive nucleotide sequences to the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes and lengthens the telomeric DNA. |
Note: The DNA polymerase can synthesize in one direction only. It works by extending the 3' end of the pre-existing nucleotide chain. Therefore, DNA polymerase moves in 3' - 5' direction along the template strand, and the daughter strand is formed in 5' - 3' direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




