
Draw a labelled sketch of sparged-stirred-tank bioreactor. Write its application.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Recombinant DNA technology is a process which involves the introduction of the foreign piece of DNA into a genome which generally contains our genes of interest. This gene which is introduced is called the recombinant gene and the technique is then called the recombinant DNA technology. Inserting this desired gene into the genome of the host is usually not as easy as it sounds. The ultimate aim of the process is to obtain a desirable protein.
Complete answer:
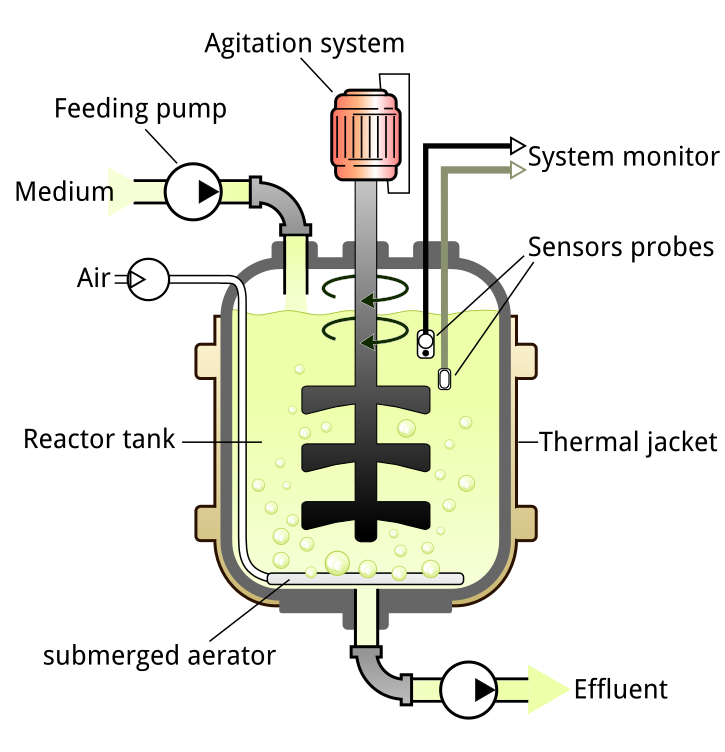
In a sparged stirred tank bioreactor ,the vessel is usually broader and flat from the bottom. Oxygen is then bubbled into the systems. Bubbles increase the oxygen transfers area and the shape provides increased surface area for the oxygen transfer.
In recombinant tech, the desired gene for administration is then selected, followed by selecting the perfect vector into which the desired gene has then to be integrated and recombinant DNA is formed. Once this foreign DNA is inserted, it is then multiplied & ultimately desirable protein is then produced. And at last, it has to be maintained in a host & carried forward to the offspring. For the production of the desired proteins, the gene gets encoded, for it needs to be expressed. This happens only under an optimised condition. Not only the target protein has to be expressed but it has to be produced on a big scale.
The recombinant cells can then be multiplied in the large scale using a continuous culture system. Here the cells are normally cultured into a large vessel and the medium is then refreshed on a regular interval to maintain the optimum conditions. This usually helps to culture a large mass of the desired protein. This tech was achieved by the development of the bioreactor.
Note: A bioreactor is usually essentially a vessel in which the raw materials are biologically converted into the specific products by efficient control of conditions like pH, Temperature, substrates or the salts, oxygen and others. It then provides optimal conditions to obtain the desired product.
Complete answer:
In a sparged stirred tank bioreactor ,the vessel is usually broader and flat from the bottom. Oxygen is then bubbled into the systems. Bubbles increase the oxygen transfers area and the shape provides increased surface area for the oxygen transfer.
In recombinant tech, the desired gene for administration is then selected, followed by selecting the perfect vector into which the desired gene has then to be integrated and recombinant DNA is formed. Once this foreign DNA is inserted, it is then multiplied & ultimately desirable protein is then produced. And at last, it has to be maintained in a host & carried forward to the offspring. For the production of the desired proteins, the gene gets encoded, for it needs to be expressed. This happens only under an optimised condition. Not only the target protein has to be expressed but it has to be produced on a big scale.
The recombinant cells can then be multiplied in the large scale using a continuous culture system. Here the cells are normally cultured into a large vessel and the medium is then refreshed on a regular interval to maintain the optimum conditions. This usually helps to culture a large mass of the desired protein. This tech was achieved by the development of the bioreactor.

Note: A bioreactor is usually essentially a vessel in which the raw materials are biologically converted into the specific products by efficient control of conditions like pH, Temperature, substrates or the salts, oxygen and others. It then provides optimal conditions to obtain the desired product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




