
Draw a neat labeled diagram of phloem.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells and together work as a single unit. Phloem is one of the complex tissues of plants.
Complete step by step answer:
Structure of phloem:
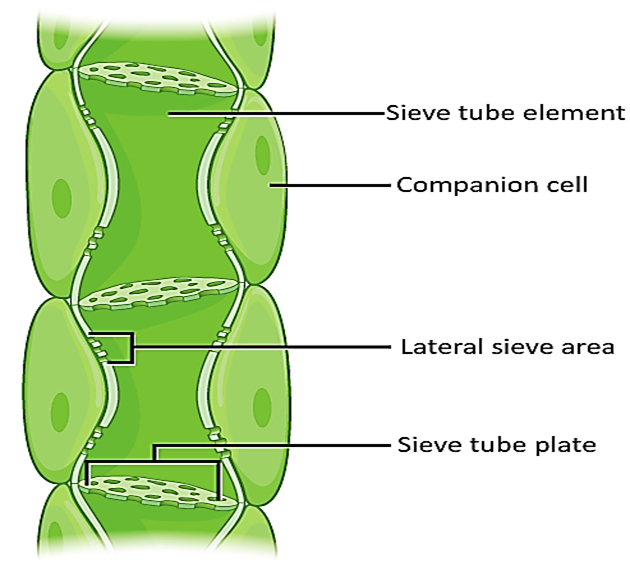
Sieve tube elements: These are long tube-like structures arranged longitudinally in association with the companion cells as shown in the above figure. They have perforated end walls in a sieve-like manner to form the sieve plates. On maturation, sieve elements possess a peripheral cytoplasm and a large vacuole but lack a nucleus. Thus, the functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
Companion cells: These are specialized parenchymatous cells that are in close association with sieve tube elements. Pit fields present between the common longitudinal walls connect sieve tube elements and companion cells. The function of companion cells is to maintain a pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
Phloem parenchyma: It has cylindrical cells having dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cell wall is made up of cellulose and has pits through which plasmodesmatal connections exist between the cells. The function of the phloem parenchyma is to store food material and other substances like resins, latex, and mucilage.
Phloem fibers: They are made up of sclerenchymatous cells. They are elongated, unbranched structures having pointed needle-like apices. The cell wall of phloem fibers is quite thick. On maturation, these fibers lose their protoplasm and become dead. Phloem fibers derived from jute, flax, and hemp are used commercially.
Note:
- The primary phloem (first- formed) consists of narrow sieve tubes known as protophloem and the later formed phloem has bigger sieve tubes and is referred to as metaphloem.
- Sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibers are the constituents of phloem in angiosperms.
- Gymnosperms have albuminous cells and sieve cells. They lack sieve tubes and companion cells.
- The monocotyledons lack phloem parenchyma.
Complete step by step answer:
Structure of phloem:
Sieve tube elements: These are long tube-like structures arranged longitudinally in association with the companion cells as shown in the above figure. They have perforated end walls in a sieve-like manner to form the sieve plates. On maturation, sieve elements possess a peripheral cytoplasm and a large vacuole but lack a nucleus. Thus, the functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
Companion cells: These are specialized parenchymatous cells that are in close association with sieve tube elements. Pit fields present between the common longitudinal walls connect sieve tube elements and companion cells. The function of companion cells is to maintain a pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.

Phloem parenchyma: It has cylindrical cells having dense cytoplasm and nucleus. The cell wall is made up of cellulose and has pits through which plasmodesmatal connections exist between the cells. The function of the phloem parenchyma is to store food material and other substances like resins, latex, and mucilage.
Phloem fibers: They are made up of sclerenchymatous cells. They are elongated, unbranched structures having pointed needle-like apices. The cell wall of phloem fibers is quite thick. On maturation, these fibers lose their protoplasm and become dead. Phloem fibers derived from jute, flax, and hemp are used commercially.
Note:
- The primary phloem (first- formed) consists of narrow sieve tubes known as protophloem and the later formed phloem has bigger sieve tubes and is referred to as metaphloem.
- Sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibers are the constituents of phloem in angiosperms.
- Gymnosperms have albuminous cells and sieve cells. They lack sieve tubes and companion cells.
- The monocotyledons lack phloem parenchyma.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




