
Draw a neat labelled diagram of antibody molecule.
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: Antibodies are protein molecules that help the immune system to recognize a foreign entity known as the antigen and remove it from the system.
Complete answer:
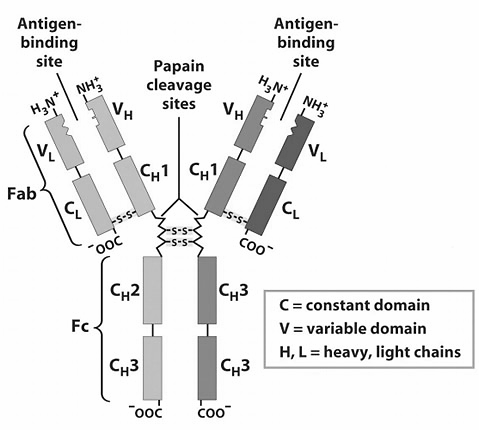
Antibody is Y-shaped in structure and comprises four polypeptide chains in humans and most other mammals. Two of these chains are known as heavy chains and two are known as light chains. The heavy and light chains are connected to each other by disulfide bonds. The light chain is known to consist of a variable and constant domain whereas the heavy chain consists of only one variable domain and four constant domains. The antibody structure is divided into two fragments- the antigen binding fragment known as Fab and the lower part of the structure that do not bind antigen and is known as Fc region. The binding of antigen takes place at the variable domain, these regions have amino acids complementary to the amino acids present at the antigen’s epitope making each antibody specific for an antigen. Antibodies are of five different types- IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE. They differ on the basis of heavy chains and are known to have different locations and carry out different biological functions.
Note:
Antibodies are capable of exerting their action by the following ways- neutralization, where they block the surface of pathogen; agglutination, where they clump foreign cells which are then targeted for phagocytosis; precipitation, similar to agglutination but here antibodies clump together and complement activation, leading to formation of membrane attack complex and cell lysis.
Complete answer:
Antibody is Y-shaped in structure and comprises four polypeptide chains in humans and most other mammals. Two of these chains are known as heavy chains and two are known as light chains. The heavy and light chains are connected to each other by disulfide bonds. The light chain is known to consist of a variable and constant domain whereas the heavy chain consists of only one variable domain and four constant domains. The antibody structure is divided into two fragments- the antigen binding fragment known as Fab and the lower part of the structure that do not bind antigen and is known as Fc region. The binding of antigen takes place at the variable domain, these regions have amino acids complementary to the amino acids present at the antigen’s epitope making each antibody specific for an antigen. Antibodies are of five different types- IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE. They differ on the basis of heavy chains and are known to have different locations and carry out different biological functions.

Note:
Antibodies are capable of exerting their action by the following ways- neutralization, where they block the surface of pathogen; agglutination, where they clump foreign cells which are then targeted for phagocytosis; precipitation, similar to agglutination but here antibodies clump together and complement activation, leading to formation of membrane attack complex and cell lysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




