
Draw a neat labelled diagram of ${H_2} - {O_2}$ fuel cell. Write the reaction that occurs at the cathode of the cell.
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy into electrical energy. Hydrogen is used as a fuel and oxygen is used as an oxidizing agent which converts electrochemical energy into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied to it.
Complete answer:
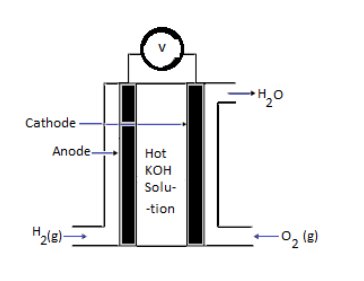
In ${H_2} - {O_2}$ fuel cell hydrogen is passed through the anode of the fuel cell and oxygen is passed through the cathode.
At the anode, the catalyst breaks the hydrogen molecules into electrons and protons.
At cathode, the following reaction takes place:
${O_{{2_{(g)}}}} + 2{H_2}{O_{(l)}} + 4{e^ - } \to 4O{H^ - }_{(aq)}$
Labelled diagram of fuel cell:
Additional information:
Some advantages of hydrogen fuel cells are: Hydrogen fuel cells are cleaner and more efficient than traditional combustion-based engines and power plants. Hydrogen and fuel cells can also be used in mobile applications to power vehicles and mobile power packs. The benefits of fuel cells are: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Note:
There are some disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells too. As hydrogen gas is expensive and it is very difficult to store the gas. It is also not easy to replace the existing infrastructure. Though it is a powerful source of fuel so hydrogen can be very flammable. As hydrogen energy is renewable and has a minimal environmental impact, other non-renewable sources such as coal, oil and natural gas are often used to separate it from oxygen. But the point of switching to hydrogen is to get rid of using fossil fuels, fossil fuels are still used to produce hydrogen fuel. Renewable energy like solar and wind can be used to generate hydrogen energy.
Complete answer:
In ${H_2} - {O_2}$ fuel cell hydrogen is passed through the anode of the fuel cell and oxygen is passed through the cathode.
At the anode, the catalyst breaks the hydrogen molecules into electrons and protons.
At cathode, the following reaction takes place:
${O_{{2_{(g)}}}} + 2{H_2}{O_{(l)}} + 4{e^ - } \to 4O{H^ - }_{(aq)}$
Labelled diagram of fuel cell:

Additional information:
Some advantages of hydrogen fuel cells are: Hydrogen fuel cells are cleaner and more efficient than traditional combustion-based engines and power plants. Hydrogen and fuel cells can also be used in mobile applications to power vehicles and mobile power packs. The benefits of fuel cells are: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Note:
There are some disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells too. As hydrogen gas is expensive and it is very difficult to store the gas. It is also not easy to replace the existing infrastructure. Though it is a powerful source of fuel so hydrogen can be very flammable. As hydrogen energy is renewable and has a minimal environmental impact, other non-renewable sources such as coal, oil and natural gas are often used to separate it from oxygen. But the point of switching to hydrogen is to get rid of using fossil fuels, fossil fuels are still used to produce hydrogen fuel. Renewable energy like solar and wind can be used to generate hydrogen energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




