
Draw a neat sketch of ruby laser. Explain its working with the help of an energy level diagram.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: A ruby laser is an instrument which is a solid-state laser that uses the synthetic ruby crystal as its laser medium. Ruby laser is the first successful laser developed. Ruby laser is one of the few solid-state lasers that are able to produce visible light. It emits a deep red light of wavelength 694.3 nm.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Working of ruby laser
The Ruby Laser consists of one crystal of ruby rod of length 10cm and 0.8cm in diameter. A ruby may be a crystal of alumina \[A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\], during which a number of aluminium ions \[\left( A{{l}^{3+}} \right)\] are replaced by the chromium ions \[\left( C{{r}^{3+}} \right)\]. The other ends of ruby rod are flat and parallel one end is fully silvered and therefore the other is partially silvered semi-transparent. The ruby rod is surrounded by a helical xenon flash tube which provides the pumping light to boost the chromium ions to upper energy level. within the xenon flash tube, each flash lasts several milliseconds and in each flash a couple of thousand joules of energy is consumed. The simplified energy state diagram of chromium ions during a ruby laser, indicating appropriate excitation and decay is shown in figure. In normal state, most of the chromium ions are within the state E1. When the ruby rod is irradiated by a flash of sunshine, photons are absorbed by the chromium ions which are pumped to the excited state E3. The excited lion gives up a part of its energy to the space lattice and decay without giving any radiation to the metastable state E2. Since the state E2 features a much longer lifetime, the amount of ions during this state goes on increasing. Thus population inversion is achieved between the states E2 and E1. When the excited ion from the metastable state E2 drops down spontaneously to the bottom state E1, it emits a photon. This photon travels through the ruby rod and is reflected back and forth by the silvered ends until it stimulates another excited ion and causes it to emit a fresh photon in phase with stimulating photons. Thus the reflections will amount to the extra stimulated emission-the so called amplification by stimulated emission. This stimulated emission is that the laser transition. Finally, a pulse of red light emerges through the partially silvered end of the crystal.
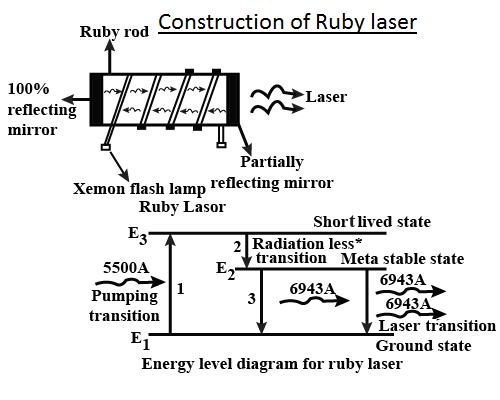
Note: Construction of ruby laser
A ruby laser consists of three important components: laser medium, the pump source, and the optical resonator.
Laser medium or gain medium in ruby laser: The ruby laser is a three level solid-state laser. In a ruby laser, optical pumping technique is used to supply energy to the laser medium.
Pump source or energy source in ruby laser: The pump source is the element of a ruby laser system that provides energy to the laser medium. In a ruby laser, population inversion is required to achieve laser emission.
Optical resonator: The ends of the cylindrical ruby rod are flat and parallel. The cylindrical ruby rod is placed between two mirrors. The optical coating is applied to both the mirrors.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Working of ruby laser
The Ruby Laser consists of one crystal of ruby rod of length 10cm and 0.8cm in diameter. A ruby may be a crystal of alumina \[A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\], during which a number of aluminium ions \[\left( A{{l}^{3+}} \right)\] are replaced by the chromium ions \[\left( C{{r}^{3+}} \right)\]. The other ends of ruby rod are flat and parallel one end is fully silvered and therefore the other is partially silvered semi-transparent. The ruby rod is surrounded by a helical xenon flash tube which provides the pumping light to boost the chromium ions to upper energy level. within the xenon flash tube, each flash lasts several milliseconds and in each flash a couple of thousand joules of energy is consumed. The simplified energy state diagram of chromium ions during a ruby laser, indicating appropriate excitation and decay is shown in figure. In normal state, most of the chromium ions are within the state E1. When the ruby rod is irradiated by a flash of sunshine, photons are absorbed by the chromium ions which are pumped to the excited state E3. The excited lion gives up a part of its energy to the space lattice and decay without giving any radiation to the metastable state E2. Since the state E2 features a much longer lifetime, the amount of ions during this state goes on increasing. Thus population inversion is achieved between the states E2 and E1. When the excited ion from the metastable state E2 drops down spontaneously to the bottom state E1, it emits a photon. This photon travels through the ruby rod and is reflected back and forth by the silvered ends until it stimulates another excited ion and causes it to emit a fresh photon in phase with stimulating photons. Thus the reflections will amount to the extra stimulated emission-the so called amplification by stimulated emission. This stimulated emission is that the laser transition. Finally, a pulse of red light emerges through the partially silvered end of the crystal.

Note: Construction of ruby laser
A ruby laser consists of three important components: laser medium, the pump source, and the optical resonator.
Laser medium or gain medium in ruby laser: The ruby laser is a three level solid-state laser. In a ruby laser, optical pumping technique is used to supply energy to the laser medium.
Pump source or energy source in ruby laser: The pump source is the element of a ruby laser system that provides energy to the laser medium. In a ruby laser, population inversion is required to achieve laser emission.
Optical resonator: The ends of the cylindrical ruby rod are flat and parallel. The cylindrical ruby rod is placed between two mirrors. The optical coating is applied to both the mirrors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




