
Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope, when the final image is formed at the minimum distance of distinct vision.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: A compound microscope is an optical instrument used for observing highly magnified images of tiny objects. The compound microscope has two lenses and it works in such a way that the image of the object from the first lens acts as the object for the second lens. A highly magnified image is thus formed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A compound microscope consists of two converging lens systems, there is an objective lens O of very small focal length and short aperture and an eyepiece E of moderate focal length and large aperture. The two lens systems in it are held co-axially at the free ends of the tube, at a suitable and fixed distance from each other. The distance of the objective lens from the object can be adjusted by the rack and pinion arrangement.
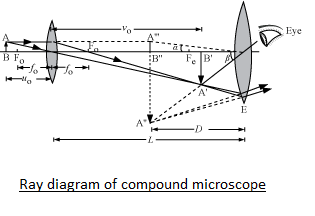
The course of rays through a compound microscopic is shown in the given figure. Here we can see that an image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision from eyes. Here, AB ia a tiny object held perpendicular to the common principal axis, in front of the objective lens beyond its focus. A real and inverted and enlarged image A’B’ of this object is formed by the objective lens which in turn acts as an object for the eye lens, whose position is adjusted so that the A’B’ lies between its optical centre and focus. A virtual and magnified image A”B” is formed by the eye lens. This image is erect with respect to A’B’ but is inverted with respect to AB.
Note: Magnifying power of the compound microscope is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the final image to the angle subtended at the eye by the object, when both the final image and the object are situated at the least distance of the distinct vision from the eyes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A compound microscope consists of two converging lens systems, there is an objective lens O of very small focal length and short aperture and an eyepiece E of moderate focal length and large aperture. The two lens systems in it are held co-axially at the free ends of the tube, at a suitable and fixed distance from each other. The distance of the objective lens from the object can be adjusted by the rack and pinion arrangement.
The course of rays through a compound microscopic is shown in the given figure. Here we can see that an image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision from eyes. Here, AB ia a tiny object held perpendicular to the common principal axis, in front of the objective lens beyond its focus. A real and inverted and enlarged image A’B’ of this object is formed by the objective lens which in turn acts as an object for the eye lens, whose position is adjusted so that the A’B’ lies between its optical centre and focus. A virtual and magnified image A”B” is formed by the eye lens. This image is erect with respect to A’B’ but is inverted with respect to AB.

Note: Magnifying power of the compound microscope is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the final image to the angle subtended at the eye by the object, when both the final image and the object are situated at the least distance of the distinct vision from the eyes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




