
Draw a ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed twice the focal length of the lens.
Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint:We will consider the simple diagram of the convex lens but with the only change in the position of the object at twice the focal length of the convex lens. After following the basic properties of refraction, the image will be formed.
Complete answer:
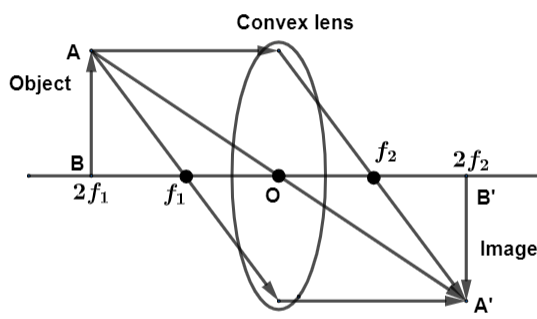
By the diagram we can clearly see that an object named AB is placed in front of the mirror. Suppose that the focal length ${{f}_{1}}$ is the focal length of the lens. We need to consider a situation in which the object is placed in the position which is twice the focal length of the lens which is $2{{f}_{1}}$. The three rays coming from the object AB are divided into three categories in which the first one passes through the by making a deviation from its path and passes through the focal point ${{f}_{2}}$. Another ray generated from the object AB passes through the center of the lens, at point O and gets through it without any deviation. The third ray passes from the bottom of the lens reaching towards the meeting of the two other rays that were mentioned before. After meeting to a same point the rays create a real and inverted image of the object namely A’B’.
Since, the object has been placed on the position which is twice its focal length so; the image that it forms is equal to the size of the object.
Note:
If the question consisted of concave in place of convex then the image would be virtual and erect. If we see that the image that is formed by the convex lens is real and inverted then this is due to the rays falling on the lens In such a way that they all meet at a point where the size of image is same as that of object. As the focal length shifts to twice the focal length of the convex lens then only we get the size of object and image as equal otherwise, the sizes would be different.
Complete answer:

By the diagram we can clearly see that an object named AB is placed in front of the mirror. Suppose that the focal length ${{f}_{1}}$ is the focal length of the lens. We need to consider a situation in which the object is placed in the position which is twice the focal length of the lens which is $2{{f}_{1}}$. The three rays coming from the object AB are divided into three categories in which the first one passes through the by making a deviation from its path and passes through the focal point ${{f}_{2}}$. Another ray generated from the object AB passes through the center of the lens, at point O and gets through it without any deviation. The third ray passes from the bottom of the lens reaching towards the meeting of the two other rays that were mentioned before. After meeting to a same point the rays create a real and inverted image of the object namely A’B’.
Since, the object has been placed on the position which is twice its focal length so; the image that it forms is equal to the size of the object.
Note:
If the question consisted of concave in place of convex then the image would be virtual and erect. If we see that the image that is formed by the convex lens is real and inverted then this is due to the rays falling on the lens In such a way that they all meet at a point where the size of image is same as that of object. As the focal length shifts to twice the focal length of the convex lens then only we get the size of object and image as equal otherwise, the sizes would be different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




